Only $0.41 per item
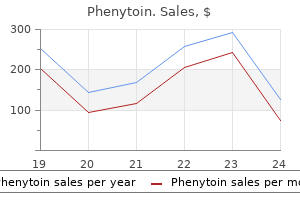
Phenytoin dosages: 100 mg
Phenytoin packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 665
8 of 10
Votes: 184 votes
Total customer reviews: 184
Description
Three-month-olds tended to direct their gaze downward from the first target symptoms zinc overdose cheap phenytoin 100 mg otc, as if directed toward a target below the current point of gaze. In reality the second target was below the first locationdthe original fixation pointdnot the current point of gaze. Seven-month-old infants, in contrast, were more likely to direct gaze directly toward the second target. The two scenarios may produce similar visual inputs from optic flow, yet we readily distinguish between them. In addition, adult observers can generally direct attention to either moving or stationary targets, nearby or in the background, as desired. These are key features of visual stability, and four eye movement systems work in concert to produce it. Because neonates and 4-month-olds appear to construe dynamic rod-and-box displays differentlydas disjoint surfaces and as occluded objects, respectivelydan important step in understanding development of perceptual completion is investigations of performance in 2-month-olds. In an initial investigation, 2-month-olds were found to show an "intermediate" pattern of performance (no reliable posthabituation preference), consistent with the possibility that spatial completion is developing at this point but not yet in final form (Johnson and Náñez, 1995). A followup study examined the hypothesis that 2-month-olds may perceive unity if given additional perceptual support. We simply increased the amount of visible rod surface revealed behind the occluder by reducing box height and by adding gaps in it, and under these conditions 2-month-olds provided evidence of unity perception (Johnson and Aslin, 1995). Adopting this approach with newborns, however, failed to reveal similar evidence: Even in "enhanced" displays, newborns seemed to perceive disjoint rather than unified rod parts (Slater et al. However, when newborns were tested with rod-and-box displays in which the rod parts appeared to "jump" from one location to the nextdthat is, apparent motion rather than smooth motiondthe infants appeared to perceive the rod parts as unified (Valenza and Bulf, 2011). These authors suggested that the smooth motion of rod parts (as tested by Slater et al. A number of studies have shown that young infants can maintain representations of the solidity and location of fully hidden objects across brief delays. Yet newborns provide little evidence of perceiving partly occluded objects, leading to the question of how perception of complete occlusion, or existence constancy, emerges during the first few months after birth. Development of the visual system Chapter 16 347 two disconnected trajectories, rather than a single, partly hidden path (Johnson et al. Reducing the spatial gap, therefore, supported perception of a complete trajectory in 4-month-olds. In 2-month-olds this manipulation appeared to have no effect, implying a lower age limit for trajectory completion. Research on face perception in infants provides additional insights on mechanisms of recognition.
Antitumor Angiogenesis Factor (anti-TAF) (Bovine Cartilage). Phenytoin.
- Treating acne.
- Dosing considerations for Bovine Cartilage.
- Treating skin conditions such as psoriasis.
- Treating poison oak and poison ivy.
- What other names is Bovine Cartilage known by?
- Treating osteoarthritis when given under the skin.
- What is Bovine Cartilage?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96192
Hollow barrels medicine rock cheap 100 mg phenytoin with mastercard, with cell sparse cores, are typical of mice, young rats, and the anterolateral subfield of mature rats, but solid columns, with cell-dense cores, are typical of the main posteromedial field in rats (Rice, 1995). Variability is not reported for other columnar systems of connections, but this is likely because many of the systems are harder to visualize globally or require specialized tissue processing. Short vertical clusters of cells are commonly observed in the deep layers of marine mammals. The cortical architecture can be missing or significantly disrupted and yet apparently remains functionally intact. For example, the disrupted barrel cortex in the reeler and in other mutant or transgenic mice is not associated with marked somatosensory deficits (Rakic and Caviness, 1995; López-Bendito and Molnár, 2003). The degree to which cortex is modifiable and, by what mechanisms, has been extensively investigated under various environmental manipulations. Although we do not know what the functional relevance (if any) of the barrel arrangements may be, this system helped the understanding of various aspects of cortical circuit formation and plasticity. Study of the barrel field in various mouse mutants proved to be instrumental in the understanding of the molecular mechanisms of these interactions (Erzurumlu and Kind, 2001). The development of the periphery-related patterning of the thalamocortical projections and the induction of the cytoarchitectonic barrels require both pre- and postsynaptic interactions. With the development of finer techniques of clonal analysis and neuronal cell-type specification, one can anticipate a new generation of genetic and molecular manipulations that will help us elucidate the underlying mechanisms of barrel formation. However, it is not clear to what extent the barrels represent a general and valid model for cortical columns. Innocenti and Vercelli (2010) distinguished minicolumns and bundles, whereas some investigators have used these terms interchangeably. Minicolumns of radially aligned cell bodies can be demonstrated by standard Nissl preparations or other histological methods that reveal cell bodies. Bundles comprise the apical dendrites of pyramidal neurons whose cell bodies are in different layers and can be seen in material prepared by the Golgi technique, stained with osmium for electron microscopical analysis or with markers of somatodendritic morphology. Innocenti and Vercelli (2010) demonstrated dendritic bundles using retrograde transport of lipophilic tracers or intracellular injection of neurons in slice preparations. Myelinated axons are also organized in bundles; these bundles course close to those of the dendrites, and at least some of them originate from neurons whose apical dendrites are in a bundle (monkey primary visual cortex: Peters and Sethares, 1996). Depending also on tangential location and depth, the minicolumns and bundles can be more or less distinct. Left panel: Schematic representation of the arrangements of the apical dendrites of pyramidal cells.
Specifications/Details
A large number of functional neuroimaging studies have demonstrated the importance of frontal regions in spatial working memory for locations treatment zone lasik 100 mg phenytoin order overnight delivery. Two regions that appear to be particularly important for spatial working memory in humans include the superior frontal cortex (Atkinson and Braddick, 2012; Courtney et al. The task of looking or reaching to a spatial location involves a complex network of neural areas within the dorsal frontoparietal system (Colby and Duhamel, 1996; Colby and Goldberg, 1999; Johnson et al. Prefrontal motor areas mediate planning and preparation for motor action; activation of these areas typically precedes the actual motor event. There is considerable evidence for superior parietal input to dorsal premotor and motor cortices; activation in frontal and superior parietal areas is concordant, suggesting a network of spatial-motor control (Rizzolatti and Matelli, 2003; Rizzolatti and Sinigaglia, 2010; Rizzolatti et al. Location processing is postulated to rely on the computation of two distinct types of relations: categorical and coordinate (Kosslyn, 1987, 2006; Kosslyn et al. Neuroimaging studies have implicated posterior parietal regions for both categorical and coordinate relational processing (Kosslyn et al. One of the largest bodies of data on the early development of visuospatial processing comes from a simple, spatial hiding task, originally introduced by Piaget (1952). Infants watch as a toy is hidden under one of two screens (A or B) and are then encouraged to retrieve it. Eight-month-olds easily retrieve the object hidden under A (but also see Smith et al. When the task requires to look rather than reach for the object, search performance is enhanced. Other factors, such as the use of salient landmarks, distinctive screens, or increased distance between the screens, also improve performance (Butterworth et al. By contrast, increasing task demands by increasing the delay between hiding and search negatively impacts performance. Introduction of a delay between hiding and retrieval increases error frequency among children as old as 12 months (Diamond, 1985; Spencer et al. Finally individual differences in temperament also affect performance (Johansson et al. Studies using near-infrared spectroscopy to measure localized brain activation in infants provide converging evidence for the association between frontal lobe development and successful search performance (Baird et al. Gamma-band activity has been associated with maintenance of mental representations of objects among adults (Tallon-Baudry et al. In summary, these data suggest that a complex network of neural systems emerge across the first year of life to support performance on this seemingly simple task. The data point to changes in both frontal and parietal regions within the dorsal stream, and suggest comparable changes within temporal and frontal regions of the ventral stream. As Johnson noted, changes within these neural regions are unlikely to be unitary events; rather, neural development likely reflects a more gradual "coming online" of the different components of the complex neural system that progressively come to support the range of behaviors involved in the visual search task (Johnson et al.
Syndromes
- The needle is removed.
- Lipid panel blood test
- Quinidine
- Loss of muscle strength
- The term can also refer to a medical procedure that removes something from an area of the body. These substances can be air, body fluids, or bone fragments. An example is removing ascites fluid from the belly area.
- Washing your skin before the test (may cause a false-negative result)
One well-characterized motif is the feedforward inhibition in L4 of barrel cortex medicine hat weather phenytoin 100 mg buy without prescription. More recently, the local network of inhibitory connectivity has been characterized in visual and somatosensory cortex. This has been suggested as one means by which focal disinhibition could be achieved during network operation. These include motor inputs from the whisker region of M1, other regions of somatosensory cortex including S2, and contralateral S1, among others. With the emergence of optical methods of specifically exciting afferents from defined neuronal population (such as excitation of corticocortical or corticothalamic afferents that express channelrhodopsin-2 [ChR2] following viral transfection) (Boyden et al. Input from the thalamus, although previously studied with conventional approaches, has also been investigated with optogenetic methods (Cruikshank et al. Corticothalamic pathways representing different aspects of incoming somatosensory information and targeting different layers originate from two thalamic nuclei. Thus, the degree to which these pathways remain segregated and where this information again converges to alter the S1 representation of touch is of some interest. The same afferents also arborize in layer 1 and may target cell types where quantification of the input is more challenging because of its distance from the soma. Inputs from contralateral S1, at least those originating from L2/3 neurons, target L2/3 and L5, which is a similar laminar pattern of output as the ipsilateral projections of these cells within the local column (Petreanu et al. The feedback projection from M1 arborizes in L1 as well as the infragranular layers. This is consistent with a corticocortical hierarchy in which feedforward output (from primary sensory areas, for example) excites the upper layers of cortical areas they target, such as L2/3 and L5A in M1 (Mao et al. Collectively, then, the past century and more of investigations has taught us much of what the basic cell types are in different layers of barrel cortex. There is still much to be learned about the connectivity of different cell types, especially as it becomes possible to trace the axons of single neurons throughout the whole brain. We furthermore have an understanding of their general patterns of local excitatory connectivity and are beginning to integrate local circuit interneurons into this understanding. This presentation is selected to emphasize differences in laminar targeting depending on the interneuron subtype. The connectivity matrix (derived from whole cellepaired recordings) shows similar connectivity with strong within-layer connections in L4 and L3. The excitatory neuronal network of the C2 barrel column in mouse primary somatosensory cortex. Inhibition of inhibition in visual cortex: the logic of connections between molecularly distinct interneurons. From a systems perspective, studies have also begun to describe the receptive fields of whisker touch.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: q.2h.
Tags: generic phenytoin 100 mg buy on line, phenytoin 100 mg purchase mastercard, buy phenytoin 100 mg without prescription, discount phenytoin 100 mg visa
Customer Reviews
Grobock, 38 years: Functionally defined white matter reveals segregated pathways in human ventral temporal cortex associated with category-specific processing. Such atypical patterns of specialization may be difficult to reverse once established.
Ines, 64 years: Afferent influences on brain stem auditory nuclei of the chicken: presynaptic action potentials regulate protein synthesis in nucleus magnocellularis neurons. Carotid arteries the main arteries that run up the anterolateral part of the neck and feed the brain blood.
Charles, 33 years: Early signatures of and developmental change in brain regions for theory of mind Chapter 21 477 are congenitally blind could help to address this question. Fearful faces but not fearful eyes alone delay attention disengagement in 7-month-old infants.