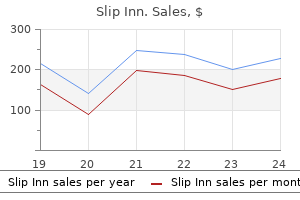
Only $1.31 per item
Slip Inn dosages: 1pack
Slip Inn packs: 10 caps, 20 caps, 30 caps, 60 caps, 90 caps, 120 caps, 180 caps
In stock: 715
9 of 10
Votes: 280 votes
Total customer reviews: 280
Description
The conjoint tendon forms the medial part of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal rumi herbals buy slip inn 1pack with visa. Notes about the Transversus Abdominis the aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis muscle takes part in forming the sheath for the rectus abdominis muscle along with those of the external and internal oblique muscles. Uppermost fibres from thoracolumbar fascia (at lateral border of the quadratus lumborum muscle) 2. Middle fibres from iliac crest (anterior two-thirds of ventral segment, intermed, zone) 3. Lowest fibres from inguinal ligament (lateral 2/3 of deep aspect) (grooved upper surface) 1. Middle fibres from thoracolumbar fascia (at lateral border of quadratus lumborum) 3. Lowest fibres from lateral 1/3 of inguinal ligament (upper grooved surface) Insertion 1. Fibres arising from lumbar inserted chiefly into linea alba from the 11th and 12th ribs end fascia and the posterior part of in an extensive aponeurosis. Fibres from anterior part of iliac pecten pubis and pubic crest) crest and lateral part of inguinal b. Its lower part is the aponeurosis has a free attached to entire length of linea lower border that forms the alba inguinal ligament. The fibres that arise from the in front of the canal, then in its 11th and 12th ribs are inserted roof, and then behind the canal. This tendon is inserted into the pubic crest and pecten pubis For all muscles: lower six thoracic nerves. Increase intra-abdominal pressure that helps to expel contents of viscera (as in defecation, micturition, vomitting and child birth) Nerve supply Action Some Structures Closely Related to Anterolateral Muscles the linea alba 1. It is formed by the interlacing of the fibres of the aponeuroses of the external oblique, the internal oblique and the transversus abdominis muscles. This is a thick curved band of fibres that lies at the junction of the abdomen and the front of the thigh. It is attached medially to the pubic tubercle and laterally to the anterior superior iliac spine (25. It represents the lower border of the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle, which is folded on itself. As a result, the ligament comes to have a grooved upper surface that can be seen if the ligament is viewed from its deep aspect. It is a triangular membrane placed horizontally, behind the medial most part of the inguinal ligament.
Brazilian Red Guava (Guava). Slip Inn.
- What is Guava?
- How does Guava work?
- Colic, diarrhea, diabetes, cough, cataracts, high cholesterol, heart disease, cancer, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Guava.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97077
As stated above the midcarpal joint is present between the proximal and distal row of carpal bones herbs mill 1pack slip inn purchase with mastercard. It is an ellipsoid joint and allows the same movements as the wrist joint, extending their range considerably. The bones taking part are the distal surface of the trapezium, and the proximal surface of the first metacarpal. The surface of the metacarpal is convex from side-to-side and concave from front to back. The movements are different from those of other digits of the hand because the thumb is rotated by ninety degrees relative to the other digits. As a result its ventral surface faces medially (not anteriorly) and its dorsal surface faces laterally (not posteriorly as in other digits). Therefore, flexion and extension of the thumb take place in a plane parallel to that of the palm, while the corresponding movements of other digits take place in planes at right angles to the palm. The remaining intercarpal, carpometacarpal, and intermetacarpal joints are all plane joints and permit slight gliding movements only. Movements at these joints are important in gripping and in all manipulative activity of the fingers. Abduction and adduction of the digits take place at the metacarpo-phalangeal joints. In abduction the index finger moves laterally, whereas the ring finger and the little finger move medially. Movement of third digit (middle finger) either medially or laterally is described as abduction. Flexion at the proximal interphalangeal joint is produced by the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus; and at the distal joint by the profundus alone. Extension of both proximal and distal interphalangeal joints is produced by the extensor digitorum, lumbricals and interossei. The extensor indicis helps in extension of the index finger, and the extensor digiti minimi in that of the little finger. Flexion of the interphalangeal joint of the thumb is produced by the flexor pollicis longus, and extension by the extensor pollicis longus. Note that flexion is associated with a certain amount of medial rotation, and extension with lateral rotation. Flexion, abduction, extension and adduction occurring in sequence constitute circumduction 156 CliniCal Correlation Part 1 Upper Extremity Dislocation can take place at any of these joints but this is not common. In clinical work, a physician wanting to examine a structure, or a surgeon planning an operation, needs to have a fairly accurate idea of where the structure lies in a living person.
Specifications/Details
Accompanying the radial nerve it passes laterally and downwards behind the humerus herbals medicine safe slip inn 1pack, where it lies in the radialgroove. The posterior descending (or middle collateral) branch descends in the substance of the medial head of the triceps and anastomoses with the recurrent branch of the posterior interosseous artery. The anterior descending (or radial collateral) artery pierces the lateral intermuscular septum and enters the anterior compartment of the arm. It runs along the radial nerve in the lower lateral part of the arm and ends by anastomosing with the recurrent branch of the radial artery. Accompanying the ulnar nerve this artery pierces the medial intermuscular septum to enter the posterior compartment of the arm. The artery ends by anastomosing with the posterior recurrent branch of the ulnar artery and with the supratrochlear artery. The supratrochlear artery (or inferior ulnar collateral artery) arises from the brachial artery a little above the elbow (5. It then runs laterally behind the humerus and anastomoses with the posterior descending branch of the profunda brachii artery and with the interosseous recurrent artery. Before piercing the medial intermuscular septum it gives off a branch that descends to anastomose with the anterior recurrent branch of the ulnar artery. In addition to the branches described above the brachial artery and its branches give off numerous muscular branches. Nutrient arteries to the humerus are given off by the brachial artery itself and by the profunda brachii branch. At its lower end the brachial artery terminates by dividing into the radial and ulnar arteries. To compress the brachial artery apply lateral pressure over the medial side of the arm immediately posterior to the medial margin of the biceps brachii. Compression of the brachial artery may occur in fracture of the shaft of the humerus (especially in supracondylar fracture) or in dislocation of the elbow joint. Fractures are very often immobilised by applying plaster casts around the affected part. A plaster cast that is too tight can be a cause of ischaemia and results can be serious if the condition is not recognised in time. Characteristic sounds heard through the stethoscope enable estimation of systolic and diastolic pressure. Ischaemia caused by sudden occlusion of the artery results in paralysis of muscles. The musculocutaneous nerve is a branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus. Reaching the lateral side of the arm it crosses in front of the lateral side of the elbow to enter the forearm. As implied by its name the musculocutaneous nerve is distributed partly to muscles and partly to skin. The muscles supplied are the coracobrachialis, the biceps brachii (both heads) and the brachialis.
Syndromes
- Esophageal manometry
- Sudden, painful, or severe facial swelling
- Long-term therapy, where you will explore your thoughts and feelings over many months or more
- Does a change in your diet make the smell worse or better?
- Are you pregnant?
- Leaky heart valves (valvular regurgitation)
- Lymph nodes in your chest may also be removed if your cancer has spread to them. The surgeon will remove them through a cut in the lower part of your neck.
- Below normal sized tonsils, lymph nodes, and spleen
- Retention of urine (unable to empty bladder)
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
This leads to a condition that is called paradoxical respiration because the lung expands during expiration and becomes smaller during inspiration herbs life discount 1pack slip inn with visa. Fluid in the pleural cavity can be aspirated by passing a needle into an intercostal space (usually the 6th) in the midaxillary line. A surgeon can enter the thoracic cavity through an opening made in the thoracic wall (thoracotomy). Depending upon the region to be approached thoracotomy can be anterior, posterior or lateral. To understand the arrangement of contents of the thoracic cavity we will begin by examining a transverse section through the cavity (19. It is more or less oval, the transverse diameter being distinctly greater than the anteroposterior diameter. Next, observe that the vertebral column projects forward into the cavity, and that on each side of it the thoracic cavity extends backwards to the level of the transverse processes of vertebrae. The backward extensions of the thoracic cavity, on either side of the vertebral column, are called the paravertebral grooves. Note the lateral walls formed by ribs and intercostal muscles; and the dome-shaped diaphragm closing the cavity inferiorly. To the right and left sides there are large spaces that are almost completely filled by the corresponding lungs. Separating the spaces for the right and left lungs there is a thick median partition that is called the mediastinum. The diaphragm is attached anteriorly to the xiphoid process, and passes backwards to reach the vertebral column at level T12. The vertical extent of the mediastinum is greater posteriorly than anteriorly (as is true for the thoracic cavity as well). The mediastinum can be divided into upper and lower parts by a horizontal plane passing from the lower end of the manubrium sterni (sternal angle) to the intervertebral disc between vertebrae T4 and T5. The part of the mediastinum lying between this plane and the inlet of the thorax is called the superior mediastinum. The part of the mediastinum lying below the superior mediastinum is divided into three parts as follows: a. The greater part of the area is occupied by the heart and by great vessels near it. At its upper end the thoracic cage has an opening that is called the superior thoracic aperture, also called the thoracic inlet.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: q.i.d.
Tags: order 1pack slip inn free shipping, slip inn 1pack order with amex, generic slip inn 1pack mastercard, buy slip inn 1pack
Customer Reviews
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Slip Inn
Volkar, 38 years: The joint is enclosed in a capsule that is strengthened in front by fibres that radiate from the head of the rib to the two vertebrae and to the intervertebral disc. In the foramen lacerum the internal carotid plexus gives off the deep petrosal nerve. The visceral layer covers the entire surface of the testis except along its posterior aspect. They are present in the presynaptic element, bind to post-synaptic receptors, and must be in sufficient quantity to affect the post-synaptic cell.
Mine-Boss, 32 years: A ballpoint pusher can be used to push the pubic portion upward and inward while the Schanz screw levers the superior acetabulum anterolaterally. The erector spinae arises from the medial surface of the dorsal segment of the iliac crest. It then runs parallel to the main artery, but along the upper border of the rib below the intercostal space. Medial to the superior orbital fissure, at the apex of the orbit, there is the opening of the optic canal.
Peer, 54 years: The deep part of the external sphincter lies external to the upper half of the internal sphincter (above the level of the pectinate line). Damped current coagulates tissue, adding to hemostasis, but causes collateral tissue damage. A little proximal to the opening, each duct shows a dilation called a lactiferous sinus. These two bones are separated by a plate of cartilage in the young, but fuse with each other in the adult.
Surus, 40 years: As the glossopharyngeal nerve winds round the stylopharyngeus it supplies this muscle. The lower ends of the lines of costomediastinal reflection (described above) are continuous with the anterior ends of the lines of costodiaphragmatic reflection which are as follows. It may be remembered that apart from narrowing of vessels, insufficiency of blood supply can also be produced by spasm of smooth muscle in the walls of arteries. In the superior radioulnar joint the ring [formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament (7.
Arokkh, 62 years: Posteriorly, the body of the sphenoid is continuous with the basilar part of the occipital bone. The interosseous talocalcaneal ligament lies deep between the talus and the calcaneus. The original tumour is the primary tumour, while the ones formed by spread from it are called secondaries. Each posterior intercostal artery gives off a number of branches that are shown in 18.
Kliff, 44 years: In paralysis of the pterygoid muscles of one side the chin is pushed to the paralysed side by muscles of the opposite side. Late dysphagia, developing months or years after surgery, is frequently due to a fibrous stricture at the site of the pharyngeal repair. Anteroinferiorly by the posterosuperior margin of the (bony) external acoustic meatus. It follows that any muscle passing from the trunk (or scapula) to the front of the humerus will be a medial rotator.