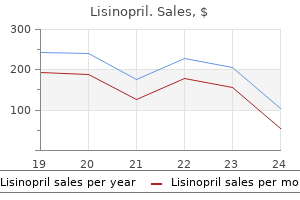
Only $0.32 per item
Lisinopril dosages: 10 mg, 5 mg, 2.5 mg
Lisinopril packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 964
10 of 10
Votes: 208 votes
Total customer reviews: 208
Description
Oral bisphosphonates are poorly absorbed hypertension 14090 buy 5 mg lisinopril mastercard, but this can be enhanced by correct administration. For example, alendronic acid tablets should be swallowed whole at least 30 minutes before breakfast or other medications, taken with plenty of water. The patient should remain upright for 30 minutes after taking to reduce oesophageal irritation. Explain that you are recommending a medicine to help strengthen the bones to prevent fractures and/or lower calcium levels in the blood to improve symptoms. To minimise this risk, give clear advice on how to take the tablets and ask them to report any symptoms of oesophageal irritation. Emphasise the dose and frequency of bisphosphonate treatment to avoid overdosing errors. For hypercalcaemia, monitor efficacy by symptom enquiry and reduction in calcium levels. For safety, be alert to symptoms of oesophagitis, osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femoral fractures, and monitor calcium and phosphate. Alendronic acid is the cheapest bisphosphonate; non-proprietary preparations cost around £1 a month. Administration Communication Monitoring Cost Clinical tip-Fragility fractures cause significant morbidity and mortality. You can assume a diagnosis of osteoporosis in women aged >75 years who have had a fragility fracture, and start treatment with a bisphosphonate without need for further investigation for osteoporosis, i. Other treatments, such as bisphosphonates, may be given to reduce the risk of fragility fractures. Calcium and vitamin D are used in chronic kidney disease to treat and prevent secondary hyperparathyroidism and renal osteodystrophy. Calcium (as calcium gluconate) is used in severe hyperkalaemia to prevent life-threatening arrhythmias. Calcium homeostasis is controlled by parathyroid hormone and vitamin D, which increase serum calcium levels and bone mineralisation, and calcitonin which reduces serum calcium levels. In osteoporosis there is a loss of bone mass which increases the risk of fracture. Restoring positive calcium balance either by dietary means or by administering calcium and vitamin D may reduce the rate of bone loss; whether this prevents fractures is less clear. In severe chronic kidney disease, impaired phosphate excretion and reduced activation of vitamin D cause hyperphosphataemia and hypocalcaemia. This stimulates secondary hyperparathyroidism, which leads to a range of bone changes called renal osteodystrophy. Treatment may include oral calcium supplements to bind phosphate in the gut, and alfacalcidol to provide vitamin D that does not depend on renal activation. In hyperkalaemia, calcium raises the myocardial threshold potential, reducing excitability and the risk of arrhythmias. The rationale for the use of calcium in hypocalcaemia and vitamin D in vitamin D deficiency is selfexplanatory.
Easter Flower (Pulsatilla). Lisinopril.
- What is Pulsatilla?
- Dosing considerations for Pulsatilla.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Pulsatilla work?
- Conditions of the male or female reproductive system, tension headache, hyperactive states, insomnia, boils, skin diseases, asthma and lung disease, earache, migraines, nerve problems, general restlessness, digestive and urinary tract problems, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96625
Serum values of aminotransferases arteria obturatoria 5 mg lisinopril purchase, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin are moderately elevated, whereas those of plasma coagulation factors are diminished. The presentation is chronic in 80% of patients; 20% of these patients progress to cirrhosis. In both conditions, acute venous obstruction is characterized by dilated centrilobular sinusoids filled with erythrocytes. Associated findings include parenchymal compression as well as atrophy and loss of hepatocytes. Erythrocytes may extravasate into the space of Disse and replace the disappearing hepatocytes. In severe cases, blood-filled lakes may form in the centrilobular zone, with little recognizable hepatic parenchyma. Hemosiderinladen macrophages may be present, but inflammation is absent to minimal. This form of fibrosis spares the portal tracts, resulting in a pattern termed reserve lobulation or venocentric cirrhosis, although end-stage cases may be indistinguishable from cirrhosis from other causes. The first symptom is abdominal pain, followed by ascites, tender hepatomegaly, jaundice, and weight gain (from fluid retention). Laboratory abnormalities include direct hyperbilirubinemia initially with subsequent elevations in alkaline phosphatase and aminotransferases. Renal dysfunction (with up to 50% of patients requiring dialysis), diuretic-resistant fluid retention, recalcitrant thrombocytopenia resulting from splenic sequestration, and encephalopathy occur later. Both sets of criteria use variable combinations of hyperbilirubinemia, weight gain, ascites, and hepatomegaly within 3 weeks of stem cell transplantation. If percutaneous biopsy is contraindicated because of thrombocytopenia, a transjugular approach may be employed, at which time the hepatic venous pressure gradient may also be measured. When elevated above 10 mm Hg, this gradient has a specificity of 90% in the appropriate clinical scenario. Asymptomatic disease occurs in patients with obstruction of only one hepatic vein or more than one hepatic vein with the development of collateral vessels. Patients classically present with ascites, hepatosplenomegaly, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Thus, the imaging evaluation should not only seek to secure the diagnosis of hepatic venous obstruction but also attempt to identify the cause of the obstruction. B, Injection of the right hepatic vein demonstrates occlusion of the vessel with numerous small collateral vessels in a characteristic spiderweb appearance. B, Equilibrium-phase image at the level of the hepatic veins continues to show this pattern of enhancement and demonstrates lack of enhancement of the vessels, consistent with occlusion (arrows). Low attenuation and heterogeneous signal intensity persist after the administration of contrast material.

Specifications/Details
Occurring in approximately 40% of patients with cirrhosis and ascites by 5 years heart attack ekg 2.5 mg lisinopril buy overnight delivery, hepatorenal syndrome is a terminal complication of cirrhosis and has a poor prognosis. In general, serum aminotransferase levels are mildly elevated (generally, <100 units/L), the total bilirubin level is proportionally elevated, and the albumin value is reduced. Because the liver synthesizes many of the blood clotting factors, the prothrombin time may be prolonged. Hyponatremia, secondary to impaired free water secretion, and renal insufficiency are seen in advanced cirrhosis and are poor prognostic signs. Once cirrhosis has been diagnosed, the severity historically has been graded by the Child-Turcotte-Pugh classification. Within 10 years, 58% of patients with cirrhosis develop various forms of hepatic decompensation. However, in early-stage cirrhosis, different hepatic insults may cause varied patterns of cirrhosis. Gross examination of the cirrhotic liver typically reveals a shrunken and firm organ, although the liver may be enlarged depending on the cause. Cirrhosis is defined histologically by the presence of fibrous septa that divide the liver parenchyma into nodules. The septa range from delicate fibrous bands to large fibrous tracts that obliterate multiple lobules. The nodules are variably sized and arbitrarily defined as micronodules (<3 mm) or macronodules (>3 mm). Occasionally, nodules may arise that are conspicuous in terms of size, color, texture, or degree of bulging from the cut surface of the liver. A, Axial computed tomography image during hepatic arterial phase after injection of intravenous contrast agent demonstrates a large, encapsulated mass in the right lobe of the liver (black arrow). Note the irregular arteries coursing through the lesion center (white arrows), a finding suggestive of hepatocellular carcinoma. B, On a more inferior slice, the right portal vein is expanded and contains linear areas of arterial hypervascularity (arrow). Although the portosystemic pressure gradient may be directly measured via transjugular cannulation of the hepatic veins, this is invasive and often unnecessary because portal hypertension can be inferred by endoscopic findings of varices and sequelae of portal hypertension seen on imaging. On cross-sectional imaging, the cirrhotic liver may demonstrate a nodular surface, widened fissures between lobes, and an increase in size of the hypertrophied caudate lobe relative to the atrophied right lobe. The ratio of caudate lobe hypertrophy to right lobe atrophy has most recently been defined by the modified ratio of caudate to right lobe, in which the lobes are divided anatomically by the bifurcation of the right portal vein. Peribiliary cysts are serous cysts that are hypothesized to represent obstructed periductal glands in patients who have severe liver disease.
Syndromes
- A person has unexplained problems with coordination
- Other symptoms of encephalitis
- Shortness of breath
- Thyroid diseases
- Skin sores (lesions)
- Roommates in dormitories
- A partial blockage can quickly become life threatening if the person cannot properly breathe.
- Spondylolisthesis, in which a bone (vertebra) in the lower part of the spine slips out of the proper position onto the bone below it
- Fanconi syndrome
- Fluids through a vein (by IV)
Pathology Initially arterial network lisinopril 5 mg otc, the appendiceal lumen occludes secondary to a number of causes, including fecaliths and lymphoid hyperplasia. Once it is occluded, intraluminal fluid continues to accumulate, distending the appendix and eventually increasing the intraluminal and intramural pressures to the point of vascular and lymphatic obstruction. Ineffective venous and lymphatic drainage allows bacterial invasion of the appendiceal wall and lumen. If this bacterial infection is not treated, perforation of the appendix and peritonitis may ensue. The appendix is considered normal when it is 6 mm or less in diameter or filled with air or oral contrast material. As the gravid uterus enlarges, the cecum, and therefore the appendix, may be in atypical locations, displaced superiorly. Color Doppler imaging may demonstrate increased vascularity of the inflamed appendiceal wall. Technical limitations of ultrasonography include difficulties imaging obese patients and the wide variety of locations of the appendix, especially those located more posteriorly within the peritoneal cavity, poses increased difficulty for evaluation. Ultrasonography is used mainly in pediatric patients, young women, and patients with small amounts of intraperitoneal fat. The lateral wall of the dilated, inflamed appendix is interrupted, and there is extraluminal gas and fluid, representing the periappendiceal abscess. B, Axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance image obtained at the same level as in A again shows the dilated appendix and inflammation of the periappendiceal fat. A, A longitudinal ultrasound image shows the blind-ending appendix is distended with fluid, and it was not compressible on the real-time examination. B, On cross section, the inflamed appendix has the typical "target" appearance, with fluid within the lumen and also adjacent to the appendix. The distended, blind-ending appendix contains an intraluminal echogenic focus at the tip, with some associated acoustic shadowing. On ultrasonography the appendix should be differentiated from loops of small bowel. Epiploic appendagitis is recognized as an ovoid lesion containing fat that abuts the colon and has surrounding inflammatory stranding, often with a central high-attenuation focus representing a thrombosed vein. In acute diverticulitis, the epicenter of the inflammatory process is an inflamed or perforated diverticulum in the ascending colon or cecum. These may be difficult to differentiate from acute appendicitis, and follow-up imaging may be necessary if the patient does not undergo surgical intervention. Other conditions, such as ureteral stones, acute biliary processes, and gynecologic diseases are discussed elsewhere in this text. Treatment the vast majority of patients with acute appendicitis are treated with surgery, increasingly performed via a laparoscopic approach.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: q.i.d.
Tags: buy 2.5 mg lisinopril mastercard, discount 2.5 mg lisinopril with amex, 5 mg lisinopril order mastercard, cheap lisinopril 2.5 mg amex
Customer Reviews
Elber, 44 years: The lifestyle intervention reduced the risk for developing kidney disease and depression with lower medical expenditures. Senzolo M, Germani G, Cholongitas E, et al: Veno-occlusive disease: update on clinical management. These disorders serve to identify patients at significant risk for development of both cardiovascular disease (main cause of death in diabetic patients) and type 2 diabetes.
Makas, 32 years: Delayed parenchymal enhancement is seen after intravenous administration of gadolinium. This is because although the serum potassium concentration is low, intake and output are in balance. You should emphasise that they may not notice immediate benefit from the inhaler, but that an improvement should be felt over hours and days.
Bengerd, 59 years: Miscellaneous Causes of Bowel Wall Thickening · Eosinophilic enteritis most commonly involves the stomach and proximal small bowel and is associated with peripheral eosinophilia. B and C, In the same imaging phases, cavernous hemangioma (vertical arrow, B) typically shows nodular, peripheral, discontinuous enhancement, which progresses centripetally. Enhancement of normal jejunal loops (arrows) is greater than that of normal ileal loops (arrowhead).
Nasib, 51 years: Open cholecystectomy is the traditional approach for surgical treatment of acalculus cholecystitis. Use of a physiologic oral glucose solution during screening for gestational diabetes mellitus. A, Longitudinal ultrasound image of the liver shows parenchymal hyperechogenicity and posterior beam attenuation.
Kasim, 45 years: The women in the control arm could have been "self-treating" by modifying their own diet on the basis of self-education. They are, therefore, the gold standard for detecting stones, evaluating strictures, and localizing bile duct leaks. Both drugs increase availability of monoamines for neurotransmission, which appears to be the mechanism whereby they improve mood and physical symptoms in moderate-to-severe (but not mild) depression.
Marcus, 65 years: With phlebotomy, there is steady disappearance of stainable iron in a pattern that is the reverse of its accumulation, from centrilobular areas to portal tracts. Diabetes and by maternal daily hyperglycemia not related to diabetes: a retrospective 10 year analysis. The common bile duct is not recognizable at the level of the lesion because of involvement, but the passage of bile in the lower segment is still maintained (arrows).
Jesper, 24 years: Effects of brief exposure to insulin-induced hypoglycemic serum during organogenesis in rat embryo culture. The latter case is of particular importance to large tumors (63% of tumors >6 cm), serosal location (17%), and prior embolization therapy. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase redistribution is associated with skeletal muscle insulin resistance in gestational diabetes mellitus.
Boss, 48 years: A prospective study comparing insulin and glibenclamide in gestational diabetes mellitus in Asian Indian women. Depending on the underlying cause, physical examination may yield additional clues. Incidence and risk factors associated with abnormal postpartum glucose tolerance in women with gestational diabetes.