Only $1.02 per item
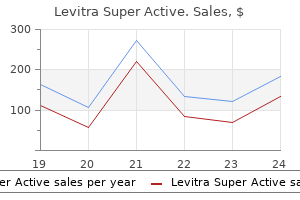
Levitra Super Active dosages: 40 mg, 20 mg
Levitra Super Active packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 996
8 of 10
Votes: 66 votes
Total customer reviews: 66
Description
Electrocardiogram shows right precordial T wave inversions and epsilon waves (arrows) erectile dysfunction at age 50 levitra super active 40 mg order amex. This diagnosis is fulfilled by the presence of two major, or one major plus two minor criteria, or four minor criteria from different groups. Definite diagnosis: two major or one major and two minor criteria, or four minor from different categories; borderline: one major and one minor, or three minor criteria from different categories; possible: one major or two minor criteria from different categories. The characteristic myocardial disarray and interstitial fibrosis provide the substrate for reentrant ventricular arrhythmias, which are probably the cause of sudden death in most patients and may be triggered or modulated by autonomic dysfunction, subendocardial ischemia, or conduction abnormalities. Recent work suggests that >15% of left ventricular fibrosis by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging is associated with increased risk of sudden death. These patients often have altered hemodynamics, abnormal cardiac chamber sizes, and reduced ventricular function. Specific conditions that have been associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac death in adulthood are the tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great arteries, and the univentricular heart. Most available data regarding risk stratification have been derived in patients with corrected tetralogy of Fallot owing to its higher prevalence. In general, these strategies, which have been demonstrated in patients with tetralogy of Fallot, are often extrapolated to patients with other congenital heart defects owing to the paucity of data in these other conditions. Patients who have incessant arrhythmias that cannot be controlled by adjuvant medical, Table 3. Note the right bundle branch block pattern with farleft axis deviation, consistent with an arrhythmia focus in the left posterior fascicle. Ablation success rates exceed 90% for this arrhythmia, so defibrillator therapy is not typically indicated. A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Use of ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring to identify highrisk patients with congenital complete heart block. Longterm follow up of children with congenital complete atrioventricular block and the impact of pacemaker therapy. Longterm survival after pacemaker implantation for heart block in patients 65 years. Intracardiac conduction defects in dystrophia myotonica: electrophysiological study of 12 cases. Prognostic importance of complete atrioventricular block complicating acute myocardial infarction. The effect of infarct size on atrioventricular and intraventricular conduction disturbances in acute myocardial infarction. Incidence and prognostic implications of 120 Cardiac Pacing, Defibrillation and Resynchronization randomized trial of permanent cardiac pacing for the prevention of vasovagal syncope.
Solsequia (Marsh Marigold). Levitra Super Active.
- What is Marsh Marigold?
- Dosing considerations for Marsh Marigold.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Pain, cramps, problems related to menstruation or "periods," bronchitis, liver problems, constipation, fluid retention, high cholesterol, low blood sugar, cleaning skin sores, and other conditions.
- How does Marsh Marigold work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96645
References 185 Identifying candidate predisposition genes the means to identify cancer predisposing genes is enabled through tumor-normal sequencing erectile dysfunction rap levitra super active 20 mg buy with mastercard. As a first step in identifying associations manifesting from mutations in cancer predisposition genes, uncertain variants in these genes can be considered for pathogenicity if detected. Integrative studies in breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and prostate cancer have revealed biallelic mutations in several known genes and some now requiring further investigation. Finally, integrative analysis links susceptibility to oncogenesis in prostate cancer and establishes functional interplay between somatic and germ line variation. A clinical guide to hereditary cancer panel testing: evaluation of gene-specific cancer associations and sensitivity of genetic testing criteria in a cohort of 165,000 high-risk patients. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Association of age at diagnosis and genetic mutations in patients with neuroblastoma. Somatic histone H3 alterations in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas and non-brainstem glioblastomas. Whole-genome sequencing identifies genetic alterations in pediatric lowgrade gliomas. Multiplatform analysis of 12 cancer types reveals molecular classification within and across tissues of origin. The genomic landscape of diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma and pediatric non-brainstem high-grade glioma. Rise and fall of subclones from diagnosis to relapse in pediatric B-acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Distinct patterns of somatic genome alterations in lung adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. The dynamic epigenetic landscape of the retina during development, reprogramming, and tumorigenesis. Comprehensive and integrated genomic characterization of adult soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer and central nervous system tumor surveillance in pediatric neurofibromatosis 2 and related disorders. Integrative analysis identifies four molecular and clinical subsets in uveal melanoma. Identification of therapeutic targets in rhabdomyosarcoma through integrated genomic, epigenomic, and proteomic analyses.
Specifications/Details
Palpation increases the risk of rupturing the spleen erectile dysfunction jack3d levitra super active 20 mg purchase with mastercard, especially if it is enlarged. Courtesy of Susan Sawyer Remember that a pelvic examination should be performed on females complaining of abdominal pain. A rectal examination should be performed on both males and females who present with abdominal pain. Diagnostic Reasoning Based on findings in the health history and physical examination, the clinician should formulate his or her assessment and plan. Table 14-4 highlights the differential diagnosis of common disorders associated with pain in the epigastrium. Gastrointestinal Assessment of Special Populations Considerations for the Pregnant Patient Note the following variations: More than 50% of pregnant women experience gastrointestinal symptoms. Morning sickness, which is nausea with or without vomiting, is common in the first trimester. It is thought to be caused by the relaxation of the gastroesophageal sphincter by progesterone. In the third trimester, heartburn is thought to be caused by pushing upward of the uterus. Digestion is delayed due to a decrease in gastric mobility and a decrease in gastric acid secretion. Considerations for the Neonatal Patient Inspection Check patency of the gastrointestinal tract, which is confirmed by the passage of meconium within the first 24 hours. Failure to pass meconium within 24 hours merits evaluation to rule out cystic fibrosis. Note that, because of the immature development of the abdominal muscles, the abdomen of a newborn is protuberant. The normal umbilical cord contains two ventrally located thick-walled arteries and one dorsally placed thinwalled vein. An umbilical hernia in a nonAfrican American infant may be indicative of hypothyroidism. Note normal percussion sounds: tympany over the intestines and dullness over the liver, feces, and full bladder. During the first month of life, the spleen is palpable 1 cm below the left costal margin. Considerations for the Pediatric Patient General Note the following: Intussusception is an acute abdominal condition caused by telescoping of the large intestine. It is the most common cause of acute abdomen for children younger than 2 years of age. The classic finding of intussusception is red currant jelly stools, which result from hematochezia. Children will not have changes in their vital signs until they are moderately to severely dehydrated. Also important to note is the urine output; amounts of less than 2 cc/kg/hr are indicative of dehydration.
Syndromes
- Problems breathing
- Cataract -- cloudiness of the eye lens
- Nuclear medicine (thallium) stress test
- Pernicious anemia
- Gestational diabetes
- Local spread of the tumor with increasing pain
- Fever
Severe grades of skeletal fluorosis are indicated to be an irreversible process in the human body impotence only with wife levitra super active 20 mg purchase line. However, few medical studies especially in children are available indicating the feasibility of its treatment and reversal, even though no mathematical analysis or modeling has been attempted by these researchers. Three published Indian double-blind clinical studies on the reversal of skeletal fluorosis in children has been analyzed to investigate the effects of increased fluoride exposure, and develop a predictive mathematical model for predicting the doses of calcium which is crucial for reversing the effects of fluoride ingestion. Bivariate analysis was used for quantitatively representing the steps involved in the pathophysiology of fluoride intake in human body. The probability of skeletal fluorosis occurrence was classified on the basis of physical parameters namely: age, weight, and fluoride intake. Oral calcium supplementation not only helps in chelating the fluoride ion in the gut forming insoluble compound calcium fluoride (CaF2), but also helps to maintain the calcium homeostasis in the body and as a net result reduces the conditions of calcium stress due to fluoride ingestion. Fluoride Ingestion causes a decrease in the ionized calcium in the human blood (hypocalcemia). This hypocalcemia changes the internal milieu of the body in order to maintain the calcium levels and leads to secondary hyperparathyroidism. It is well known that ionic calcium is one of the important ions for the initiation and maintenance of the activity of the vital organs and musculoskeletal system. The calcium circulation process in the human system is controlled by the following two mechanisms [8]: 1. Calcium balance by absorption in intestine; and Calcium excretion by kidney into urine. Along with the intestine and kidney, the skeleton has the major role in calcium homeostasis and therefore any regulatory changes in the calcium level in circulation would have a significant impact on bone metabolism. Any prolonged calcium stress in the human body which may sometimes be caused due to insufficient dietary calcium intake, may cause disturbance in the in-vivo availability of calcium as well as its absorption causing deleterious effects on the skeletal system or the bone mass. Significant Loss of Bone Mass: Bone loss is due to increase in the number of osteoblasts and the increase of their activity [9, 10] which causes the stimulation of bone resorption and depletion of bone mass as well as its formation. Under the normal conditions, where there is an increase in bone resorption, it gets coupled with an effective compensatory increase in an equal magnitude of bone formation and therefore no net bone mass is depleted in the skeletal system. However, during the adjustor mechanism if there is a demand to mobilize calcium from skeletal system to counteract the effects of hypocalcemia, then the bone coupling process gets compromised. Therefore, the combination of various combined actions such as calcium depletion, bone resorption and decrease in its formation led to a significant loss of bone mass [9]. To summarize the above mechanisms, prolonged fluoride ingestion will cause hypocalcemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism causing increased bone resorption, defective collagen formation, and defective bone formation which explains all the clinical, dental, and skeletal presentations of fluorosis. It is therefore hypothesized that all these effects are mediated through hyperparathyroidism secondary to increased fluoride ingestion.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: q._h.
Tags: generic levitra super active 20 mg buy, generic 40 mg levitra super active otc, buy generic levitra super active 40 mg, best 20 mg levitra super active
Customer Reviews
Phil, 22 years: This makes setting the allele frequency benign evidence cutoff at half the prevalence of the disorder a very conservative approach as well.
Ateras, 56 years: Alternatively, a hand can be placed over the appropriate hemidiaphragm to feel for diaphragmatic stimulation.