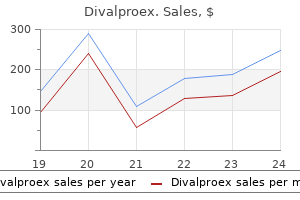
Only $0.62 per item
Divalproex dosages: 500 mg, 250 mg
Divalproex packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 863
8 of 10
Votes: 319 votes
Total customer reviews: 319
Description
Differential diagnosis of parkinsonism with visual inspection of posture and gait in the early stage medications j-tube best 250 mg divalproex. Multiple system atrophy presenting as parkinsonism: clinical features and diagnostic criteria. Accuracy of clinical criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome). Accuracy of the National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke/Society for Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and neuroprotection and natural history in Parkinson plus syndromes criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy. Different clinical and evolutional patterns in late idiopathic and vascular parkinsonism. Neurological signs and frontal white matter lesions in vascular parkinsonism: a clinicopathologic study. Certain additional findings, however, may distinguish hemorrhagic from ischemic stroke. In the United States, 87% of strokes are ischemic and 13% are hemorrhagic (10% are intracerebral and 3% are subarachnoid),1 but in some developing nations more than 50% of strokes are hemorrhagic. Top half: There is a small hemorrhage in the left basal ganglia, causing hemiparesis and clinical findings indistinguishable from ischemic stroke. Bottom half: Progressive intracranial hemorrhage causes the "additional" findings of hemorrhage, including rapid neurologic deterioration, headache, vomiting, coma, and neck stiffness. Intraventricular blood follows the normal path of cerebrospinal circulation through the median and lateral apertures of the fourth ventricle to reach the subarachnoid space at the base of the brain (only rarely does intracerebral hemorrhage directly rupture in the subarachnoid space). Examples of additional symptoms are prominent vomiting (from increased intracranial pressure), severe headache (from meningeal irrigation or increased intracranial pressure), rapid progression of neurologic deficits (from expansion of the hematoma), coma (from bilateral cerebral dysfunction, uncal herniation, or posterior fossa mass effect), and bilateral Babinski signs (from bilateral dysfunction). Over the last several decades, clinicians have developed several different stroke scores to distinguish hemorrhagic from ischemic infarction,3 but the most widely used is the Siriraj stroke score, developed by Poungvarin et al. The diagnosis of hemorrhagic stroke in these studies includes intracranial and subarachnoid hemorrhage, although relatively few patients had subarachnoid hemorrhage. The diagnostic accuracy of bedside findings is the same if patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage are excluded. As expected (see the section on Findings), the presence or absence of neurologic deficits-hemiparesis, hemisensory disturbance, deviation of eyes, aphasia, hemianopia, and ataxia-fail to distinguish hemorrhagic from ischemic stroke. Heart disease and stroke statistics 2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Siriraj stroke score and validation study to distinguish supratentorial intracerebral haemorrhage from infarction. The Lausanne stroke registry: analysis of 1000 consecutive patients with first stroke.
Strangle Tare (Dodder). Divalproex.
- How does Dodder work?
- Dosing considerations for Dodder.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Bladder, liver, and spleen problems.
- What is Dodder?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96067
In patients with known dilated cardiomyopathy and severe left ventricular dysfunction treatment 2 degree burns divalproex 500 mg order, a proportional pulse pressure. Subsequently, clinicians have used physical examination to classify hospitalized patients with heart failure into the same four profiles. In general, cold patients have signs of compromised perfusion, such as cool extremities, narrow proportional pulse pressure (<25%; see Chapter 17), pulsus alternans (see Chapter 15), symptomatic hypotension, and impaired mentation. Blood pressure responses to the Valsalva maneuver in cardiac patients with and without congestive failure. Is blood pressure response to the Valsalva maneuver related to neurohormones, exercise capacity, and clinical findings in heart failure A new method of predicting pulmonary capillary wedge pressure: the arterial pressure ratio. Accurate detection of elevated left ventricular filling pressure by a simplified bedside application of the Valsalva maneuver. Tachycardia during the Valsalva maneuver: a sign of normal diastolic filling pressures. Relationship between accurate auscultation of a clinical useful third heart sound and level of experience. Detection of left ventricular dysfunction in ambulatory subjects with the bedside Valsalva maneuver. Evaluation of a noninvasive system for determining left ventricular filling pressure. Noninvasive determination of pulmonary artery wedge pressure in patients with chronic heart failure. Prognostic implications of the blood pressure response to the Valsalva maneouvre in elderly cardiac patients. Utility of B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure in an urgent-care setting. Diagnostic value of B-type natriuretic peptide and chest radiographic findings in patients with acute dyspnea. Comparative value of Doppler echocardiography and B-type natriuretic peptide assay in the etiologic diagnosis of acute dyspnea. The combined utility of an S3 heart sound and B-type natriuretic peptide levels in emergency department patients with dyspnea. S3 detection as a diagnostic and prognostic aid in emergency department patients with acute dyspnea. Utility of a rapid B-natriuretic peptide assay in differentiating congestive heart failure from lung disease in patients presenting with dyspnea. The diagnostic value of physical examination and additional testing in primary care patients with suspected heart failure. Clinical determinants of mortality in chronic congestive heart failure secondary to idiopathic dilated or to ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Specifications/Details
Examination of facial nerve function Sitting level with the patient medications enlarged prostate purchase divalproex 500 mg line, examine their general appearance and for any scars or masses. Remember that there is crossover in the innervation of this region so that a patient is still able to wrinkle their forehead in a unilateral upper motor neuron palsy. Ask the patient to shut their eyes tightly, flare their nostrils, blow out their cheeks and bare their teeth. Where facial weakness is observed, blinking repeatedly may reveal synkinesis where reinnervation has occurred along incorrect pathways; contraction of obicularis oris muscle may result in contraction of the angle of the mouth. It is common, extremely painful and often precipitated by irritants such as cotton buds. There may be an infective component, commonly bacterial, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Proteus, or less frequently fungal, such as Aspergillus species or Candida albicans. The external auditory canal is often swollen and filled with debris that requires microsuction. Treatment generally consists of one week of ear drops containing a combination of steroid and antibiotic. An ear swab is useful in directing antibiotic selection where the infection does not resolve with the initial treatment. When the external ear canal is very swollen, a wick is inserted to splint the meatus open to allow penetration of the topical treatment. The infection may progress to involve the pinna and peri-auricular soft tissues (cellulitis), necessitating hospital admission for intravenous antibiotics. An important differential diagnosis of otitis externa is malignant otitis externa. This is an osteomyelitis of the ear canal and lateral skull base, which occurs more frequently in diabetics and immunocompromised patients presenting with severe pain. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common cause and the typical otoscopic appearance is granulation tissue or exposed bone on the floor of the ear canal. Treatment is a prolonged course of intravenous antibiotics followed by further oral antibiotics (twelve week), regular microsuction, topical antibiotic-steroid ear drops, good glycaemic control and analgesia. A biopsy is often needed to exclude malignancy and determine microbiological sensitivities. Although often asymptomatic, it may cause a conductive hearing loss and discomfort. Impacted wax needs to be removed to facilitate examination of the tympanic membrane. In primary care, removal is facilitated by the use of ceruminolytic agents (2) or ear syringing. Syringing is, however, contraindicated in those who have a tympanic membrane perforation or who have developed otitis externa from previous syringing. In otolaryngology departments wax is removed under the microscope using a Zoellner sucker, wax hook, JobsonHorne probe or crocodile forceps. The use of cotton buds by the patient should be discouraged as this impacts wax and traumatises the ear canal causing otitis externa.
Syndromes
- Radical neck dissection: All the tissue on the side of the neck from the jawbone to the collarbone is removed. The muscle, nerve, salivary gland and major blood vessel in this area are all removed.
- Dark urine
- A new seizure without an obvious cause
- The government gathers and reports information about hospitals. You can find this information online at www.hospitalcompare.hhs.gov.
- Laxative
- Awakening at night short of breath
Keywords: postoperative complications medications you should not take before surgery divalproex 250 mg buy, dermatitis, hematoma, infection, corneal injuries, chondritis, flap failure, wound disruption occurs in the initial postoperative period, there can be little downside to immediately returning to the operating room, identifying the bleeding source, and evacuating the hematoma. If a hematoma occurs in the immediate perioperative period but after patient discharge, the criteria for returning to the operating room for evacuation is similar but not as urgent. There is almost always some negative impact on the final repair appearance whether it is a color mismatch or contour irregularity, but it always carries with it an increased risk of postoperative infection if left undrained. Although gratifyingly rare, appropriate treatment of softtissue infections on the face requires accurate identification of the involved pathogen. Although nearly universal in use, prolonged application of topical antibiotic ointment results in a very high incidence of dermatitis. The early identification and effective treatment of chondritis is necessary to prevent long-term ear deformity. Antibiotic therapy for mild to moderate cases can be initiated with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole or doxycycline pending culture results, while severe purulent and moderate to severe nonpurulent cellulitis requires admission with intravenous antibiotics. The reconstructive surgeon needs to be adept at identifying which patients and procedures can be managed with anticoagulation. Additionally, the surgeon should be well versed with the use of a wide range of intraoperative techniques for safe hemostasis during awake anesthesia, including wide infiltration with epinephrine containing local anesthetics, and the use of topical oxidized cellulose. Fibrinous exudate illustrated is consistent with characteristic of normal wound healing with Integra and is not an infectious process. Exudate is removed and split-thickness skin graft is performed as planned with 100% graft take. She developed postoperative infection that was treated with a course of oral antibiotics. Final results shown at 1 month with no negative sequelae as a result of the infection. Rash rapidly resolved with cessation of topical ointment with no long-term sequelae. Treatment required intravenous antibiotics with multidrug coverage for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This flap design is inherently poor because it converts an axial-pattern flap unnecessarily to a random pattern flap. Additionally, the transverse brow incision both irreversibly elevates the contralateral eyebrow and renders the contralateral brow useless for a rescue flap. For a surgeon, losing one flap is devastating, but losing a second "rescue" flap is an order of magnitude more devastating for the patient as it is frequently the last chance at a reasonable reconstruction that is lost. Evaluation of a flap in jeopardy during the immediate postoperative period should include patient assessment and removal of any flap dressings that may contribute to venous or arterial compression. Additionally, evaluation of the flap pedicle to ensure no compression and removal of a portion of the inset sutures may promote flap survival. For flaps with venous congestion, the use of topical nitroglycerin ointment is beneficial, as is the use of leech therapy, but the utilization of hyperbaric oxygen or intravenous anticoagulants is of questionable benefit and of significant expense. Wound Disruption Something that occurs infrequently, but is devastating when it does, is complete wound disruption or flap disruption from inset pedicled flaps or local flaps.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: b.i.d.
Tags: purchase 250 mg divalproex otc, buy generic divalproex 500 mg line, generic divalproex 500 mg online, divalproex 500 mg buy without prescription
Customer Reviews
Fraser, 49 years: The murmur containing the highest frequency sound is aortic regurgitation, whose dominant frequencies are approximately 400 Hz. First, orthopnea is uncommon in other disorders with similar reductions of vital capacity and compliance. Pseudocyanosis may occur after exposure to metals (argyria from topical silver compounds; chrysiasis of gold therapy) or drugs (amiodarone, minocycline, chloroquine, or phenothiazines). The Austin Flint murmur: its differentiation from the murmur of rheumatic mitral stenosis.
Josh, 41 years: The quadruple rhythm typically occurs in patients who have had a longstanding S4 gallop from ischemic or hypertensive heart disease but who then develop cardiac decompensation, high filling pressures, and an S3. Clinical features Increased sebum production by sebaceous glands, blockage of pilosebaceous units, follicular epidermal hyperproliferation and infection with Propionibacterium acnes all contribute to produce the clinical features of open comedones (blackheads) or closed comedones (whiteheads), inflammatory papules and Common skin conditions 811 pustules. Visual loss Every patient with unexplained visual loss requires ophthalmic referral. Atherosclerosis results in stroke, ischaemic heart disease and peripheral vascular disease.
Fadi, 62 years: On examination there may be no physical signs; there may be weakness and wasting of the thenar muscles and sensory loss of the palm and palmar aspects of the radial three and a half fingers. According to traditional teachings, bacterial conjunctivitis is more likely if disease onset is during the winter months or if there is a purulent exudate,4 which may cause stickiness of the eyelids in the morning. Long-standing hypopituitarism may give the classic picture of pallor with hairlessness (alabaster skin). Differential diagnosis Thyroid ophthalmopathy, myotonic dystrophy and brainstem cranial nerve lesions present with ocular and/or bulbar symptoms.