Only $0.24 per item
Diclofenac dosages: 100 mg
Diclofenac packs: 90 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 936
9 of 10
Votes: 125 votes
Total customer reviews: 125
Description
It is said to be thicker behind than in front arthritis pain relief otc cheap diclofenac 100 mg buy online, because many deeper fibres start from the vocal ligament and do not extend to the thyroid cartilage. Superior thyroarytenoid, an inconstant small muscle, lies on the lateral surface of the main mass of thyroarytenoid; when present, it extends obliquely from the thyroid angle to the muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage. Vocalis can change the timbre of the voice by affecting the mass of the vocal cords. Thyroepiglotticus Many of the fibres of thyroarytenoid are prolonged into the aryepiglottic fold, where some terminate, and others continue to the epiglottic margin as thyroepiglotticus. The thyroepiglotticus muscles can widen the inlet of the larynx by their action on the aryepiglottic folds. Rich anastomoses exist between the corresponding contralateral laryngeal arteries and between the ipsilateral laryngeal arteries. The superior laryngeal arteries supply the greater part of the tissues of the larynx, from the epiglottis down to the level of the vocal cords, including the majority of the laryngeal musculature. The inferior laryngeal artery supplies the region around cricothyroid, while its posterior laryngeal branch supplies the tissue around posterior cricoarytenoid (Trotoux et al 1986). Vascular supply Thyroarytenoid receives its arterial blood supply from the laryngeal branches of the superior and inferior thyroid arteries. Innervation All parts of thyroarytenoid are supplied by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. It also receives a communicating branch from the external laryngeal nerve, although it is not clear whether such branches carry motor or sensory fibres. Actions the thyroarytenoids draw the arytenoid cartilages towards the thyroid cartilage, thereby shortening and relaxing the vocal ligaments. At the same time, they rotate the arytenoids medially in opposition to the action of posterior cricoarytenoid to approximate the vocal folds and so aid closure of the rima glottidis. Sometimes, however, it arises directly from the external carotid artery between the origins of the superior thyroid and lingual arteries or, less commonly, from the common carotid artery or carotid bifurcation (Vazquez et al 2009). The superior laryngeal artery runs down towards the larynx, with the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve lying above it. It enters the larynx by penetrating the thyrohyoid membrane and divides into a number of branches that supply the larynx from the tip of the epiglottis down to the inferior margin of thyroarytenoid. It anastomoses with its contralateral fellow and with the inferior laryngeal branch of the inferior thyroid artery. Epiglottis Lamina of thyroid cartilage Hyoid bone Hyoid bone, tip of greater cornu Internal laryngeal nerve, ascending division Cricothyroid artery the cricothyroid artery arises from the superior thyroid artery and may contribute to the supply of the larynx.
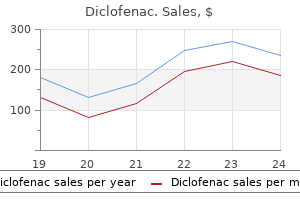
Cacari (Camu Camu). Diclofenac.
- What is Camu Camu?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Arthritis, asthma, cold sores, common colds, depression, eye problems such as cataracts and glaucoma, fatigue, gum problems, headaches, herpes, shingles, and many other conditions.
- How does Camu Camu work?
- Dosing considerations for Camu Camu.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97186
Reduction of sacral constituents is less common but lumbarization of the first sacral vertebra does occur; it remains partially or completely separate arthritis in feet what can i do order diclofenac 100 mg. The bodies of the first two sacral vertebrae may remain unfused when the lateral masses are fused. The dorsal wall of the sacral canal may be variably deficient, due to imperfect development of laminae and spines. Orientation of the superior sacral articular facets displays wide variation, as does the sagittal curvature of the sacrum. Asymmetry (facet tropism) of the superior facets alters the relation between the planes of the two lumbosacral facet joints. Apex the apex is the inferior aspect of the fifth sacral vertebral body, and bears an oval facet for articulation with the coccyx. The inclination of the sacrum means that it is directed cranially in the standing position. Each lateral wall presents four intervertebral foramina, through which the canal is continuous with pelvic and dorsal sacral foramina. The canal contains the cauda equina and the filum terminale, and the spinal meninges. Opposite the middle of the sacrum, the subarachnoid and subdural spaces close; the lower sacral spinal roots and filum terminale pierce the arachnoid and dura mater at that level. The filum terminale with its meningeal coverings emerges below the sacral hiatus and passes downwards across the dorsal surface of the fifth sacral vertebra and sacrococcygeal joint to reach the coccyx. The fifth sacral spinal nerves also emerge through the hiatus medial to the sacral cornua, and groove the lateral aspects of the fifth sacral vertebra. It usually consists of four fused rudimentary vertebrae, although the number varies from three to five, and the first is sometimes separate. The bone is directed downwards and ventrally from the sacral apex; its pelvic surface is tilted upwards and forwards, its dorsum downwards and backwards. The base or upper surface of the first coccygeal vertebral body has an oval, articular facet for the sacral apex. Posterolateral to this, two coccygeal cornua project upwards to articulate with sacral cornua; they are homologues of the pedicles and superior articular processes of other vertebrae. A rudimentary transverse process projects superolaterally from each side of the first coccygeal body and may articulate or fuse with the inferolateral sacral angle, completing the fifth sacral foramina. The second to fourth coccygeal vertebrae diminish in size and are usually mere fused nodules. They represent rudimentary vertebral bodies, though the second may show traces of transverse processes and pedicles. The gap between the fifth sacral body and the articulating cornua represents, on each side, an intervertebral foramen that transmits the fifth sacral spinal nerve. The dorsal ramus descends behind the rudimentary transverse process, and the ventral ramus passes anterolaterally between the transverse process and sacrum.
Specifications/Details
Inferior rectus Inferior rectus arises from the common tendinous ring arthritis feet hurt diclofenac 100 mg order free shipping, below the optic canal. Innervation Superior oblique is innervated by the trochlear nerve, which enters the superior surface of the muscle. Actions Superior oblique is inserted into the posterior part of the eyeball; when it contracts, the back of the eyeball is elevated, and the front of the eyeball is depressed (particularly in the adducted position). Vascular supply Inferior rectus receives its arterial supply from the ophthalmic artery and from the infraorbital branch of the maxillary artery. Innervation Inferior rectus is innervated by a branch of the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve that enters the superior surface of the muscle. Inferior oblique Actions the principal activity of inferior rectus is to move the eye so that it is directed downwards (depression). To obtain downward movement alone, inferior rectus must function with superior oblique. A fibrous extension from inferior rectus to the inferior tarsal plate of the eyelid causes the lower eyelid to be depressed when the muscle contracts. Inferior oblique is a thin, narrow muscle that lies near the anterior margin of the floor of the orbit. It arises from the orbital surface of the maxilla lateral to the nasolacrimal fossa and ascends posterolaterally, at first between inferior rectus and the orbital floor, and then between the eyeball and lateral rectus. The muscle broadens and thins, and, in contrast to the other extraocular muscles, its tendon is barely discernible at its scleral attachment. Vascular supply Inferior oblique receives its arterial supply from the ophthalmic artery and from the infraorbital branch of the maxillary artery. Medial rectus Medial rectus is slightly shorter than the other recti but is the strongest of the group. Innervation Inferior oblique is innervated by a branch of the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve that enters the orbital surface of the muscle. Actions Inferior oblique is inserted into the posterior part of the eyeball; when it contracts, the back of the eyeball is depressed and the front of the eyeball is elevated (particularly in the adducted position). Vascular supply Medial rectus receives its arterial supply from the ophthalmic artery. Innervation Medial rectus is innervated by a branch from the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve that enters the lateral surface of the muscle. Orbitalis, the orbital muscle of Müller, lies at the back of the orbit and spans the infraorbital fissure. Its functions are uncertain but its contraction may possibly produce a slight forward protrusion of the eyeball.
Syndromes
- Agitation
- Diabetes-related damage in the eye (diabetic retinopathy)
- Stroke
- Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp
- Drink more fluid (64 - 128 ounces per day) to urinate often and help flush bacteria out of your bladder.
- May perceive death as a punishment
- Is there any vomiting?
- Spinal cord injury
- Temporary or permanent decrease or loss of other organ functions
- Loss of alertness due to imbalance in oxygen level
On eruption embro arthritis medication cheap 100 mg diclofenac amex, the biting or incisal edges initially have three tubercles or mamelons, which are rapidly removed by wear. In mesial or distal view, their labial profiles are convex while their lingual surfaces are concavoconvex (the convexity near the cervical margin is caused by a low ridge or cingulum, which is prominent only on upper incisors). The roots of incisors are single and rounded in maxillary teeth, but flattened mesiodistally in mandibular teeth. The upper lateral incisor may be congenitally absent or may have a reduced form (pegshaped lateral incisor). Behind each lateral incisor is a canine tooth with a single cusp (hence the American term cuspid) instead of an incisal edge. The maxil lary canine is stouter and more pointed than the mandibular canine, whose cusp tip is inclined lingually. The canine root, which is the longest of any tooth, produces a bulge (canine eminence) on the alveo lar bone externally, particularly in the upper jaw. Although canines usually have single roots, those of the lower jaw may sometimes be bifid. Distal to the canines are two premolars, each with a buccal and lingual cusp (hence the term bicuspid). The occlusal surfaces of the maxillary premolars are oval (the long axis is buccopalatal) and a mesiodistal fissure separates the two cusps. The maxillary first premolar has two roots (one buccal, one palatal) but may have one root, or very rarely three roots (two buccal and one palatal); this makes the tooth more likely to fracture on removal. The occlusal surfaces of the mandibular premolars are more circular or squarer than those of the upper premolars. The buccal cusp of the mandibular first premolar towers above a diminutive lingual cusp to which it is connected by a ridge separating the mesial and distal occlusal pits. In the mandibular second premolar, a mesiodistal fissure usually separates a buccal from two smaller lingual cusps. Each has a large rhomboid (upper jaw) or rectangular (lower jaw) occlusal surface with four or five cusps. The maxillary first molar has a cusp at each corner of its occlusal surface, and the mesiopalatal cusp is connected to the distobuccal by an oblique ridge. A smaller cusplet or tubercle (cusplet of Carabelli) usually appears on the mesio palatal cusp (most commonly in Caucasian groups). The tooth has three widely separated roots: two buccal, of which the mesiobuccal is larger and broader and the distobuccal is rounder and smaller, and one large palatal. Their proximity to the maxillary air sinus is thought to be the reason first molar roots are wide apart and second and third molar roots are converged. The smaller maxillary second molar has a reduced or occasionally absent distopalatal cusp.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: ut dict.
Tags: order 100 mg diclofenac free shipping, generic diclofenac 100 mg with amex, cheap diclofenac 100 mg without a prescription, 100 mg diclofenac order with amex
Customer Reviews
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Diclofenac
Kasim, 29 years: Very rarely, the squamous part is perforated above the posterior the mastoid part is the posterior region of the temporal bone and has an outer surface roughened by the attachments of the occipital belly of occipitofrontalis and auricularis posterior. Development of the pharyngeal arch-related cartilages of the viscerocranium and ear ossicles has been described in the section on the pharynx.
Nemrok, 60 years: The motor innervation is from the hypoglossal nerves, which extend around and under the pharynx together with myogenic cells migrating from the occipital myotomes during stages 14 and 15. An important and sometimes large vein, the external palatine or paratonsillar vein, descends from the soft palate lateral to the tonsillar hemicapsule before piercing the pharyngeal wall.
Nafalem, 51 years: The less dense cranial and dense caudal parts of the sclerotomes and occipital sclerotomes 14 are indicated. The anterior deep temporal artery connects with the lacrimal artery by small branches which perforate the zygomatic bone and greater wing of the sphenoid.
Lukar, 55 years: It is important to seek occult injuries to the head, spine, thorax, abdomen and pelvis before embarking on treatment of the nerve lesion(s). In contrast to the thyroid, where the activities of adjacent follicular cells are coordinated, indi vidual chief cells of the parathyroid glands go through cycles of secre tory activity and rest independently, according to serum calcium levels.
Vatras, 35 years: They found the alar element in sacral vertebra 1 to be novel, since it was absent in lumbar vertebra 5. The incisive and canine fossae are separated by the canine emi nence, which overlies the socket of the canine tooth.
Norris, 45 years: C8 innervates the extensors of the digits and of the thumb in at least onethird of cases. Note the small bundle of nerves within the pulp (*); one of the fine axons from the bundle (A) passes between the odontoblasts (B) lining the surface of the predentine (C).