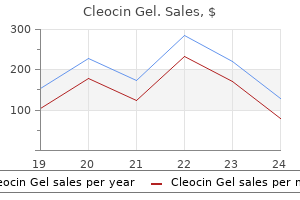
Only $15.09 per item
Cleocin Gel dosages: 20 gm
Cleocin Gel packs: 2 creams, 3 creams, 4 creams, 5 creams, 6 creams, 7 creams, 8 creams, 9 creams, 10 creams
In stock: 546
8 of 10
Votes: 51 votes
Total customer reviews: 51
Description
Renal Manifestations Renal involvement is usually manifested by proteinuria skin care doctors 20 gm cleocin gel overnight delivery, active urinary sediment with microhematuria, dysmorphic erythrocytes and erythrocyte casts, and hypertension. Clinical findings correlate well with histologic glomerular findings (see later discussion). Older lupus patients may present with joint deformities typical of rheumatoid arthritis. Serositis, in the form of pleuritis or pericarditis, affects up to 40% of patients. Libman Sacks endocarditis and much more common mitral valve prolapse can be detected with clinical findings or by echocardiography. Thrombocytopenia and leukopenia may be part of the disease process or may result from complications of therapy. Sm antibodies are strongly associated with the diagnosis of lupus and the presence of nephritis but are present in only about 25% to 30% of patients. Either both C3 and C4 are depressed or C4 is preferentially depressed in lupus patients, usually reflecting pref erential activation of the classical complement pathway. Alternatively, low C4 with normal C3 may reflect genetic C4 deficiency in lupus patients or the presence of cryoglobulins. This is partly a result of the varied features of the disease and the evolution of signs and symptoms over time. Light microscopy is normal, but immunoperoxidase shows C1q localization (associated with IgG and C3) throughout the mesangial area. A, Mesangial expansion but little increase in tuft cellularity, and the peripheral capillary walls are normal. The membranous alterations may be present alone or on a back ground of mesangial hypercellularity and mesangial immune depos its. B, Immunoperoxidase staining shows dense, irregular aggregates of IgG along the peripheral capillary walls. C, Electron microscopy reveals the immune aggregates as electron-dense deposits (arrows), predominantly in the subendothelial location. More than half of patients have significant T cellB cell aggre gates in the renal interstitium, and a small percentage have typical appearing germinal centers. In chronic disease, the interstitium is expanded by fibrosis and sparser infil trates. B, Silver methenaminestained section shows some double contouring of the silver-positive basement membrane (arrow) and subendothelium-deposited material as well as the characteristic silver-positive spikes of basement membranelike material.
Henna (Alkanna). Cleocin Gel.
- Skin diseases, healing leg ulcer wounds, stomach ulcers, and diarrhea.
- How does Alkanna work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Dosing considerations for Alkanna.
- What is Alkanna?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96601
Renal dysplasia acne 26 year old female cheap cleocin gel 20 gm buy, although typically producing small, irregular kidneys, may be cystic or multicystic renal dysplasia. Renal Dysplasia Renal Hypoplasia (Oligomeganephronia) Renal hypoplasia is defined as a congenitally small kidney (two standard deviations below the expected mean) that lacks evidence of either parenchymal maldifferentiation (renal dysplasia) or acquired disease sufficient to explain the reduced size. The term is often used loosely, however, and most patients with a small kidney and other malformations will have oligomeganephronia. This is a type of renal hypoplasia resulting from a congenital reduction in the number of nephrons. It results from arrested development of the metanephric blastema at 14 to 20 weeks of gestation with subsequent hypertrophy of glomeruli and tubules in the kidney. The hypertrophy and hyperfiltration result in progressive nephron injury and sclerosis later in life. Oligomeganephronia is recognized on renal biopsy by the large size of the glomeruli and tubules and the small number of glomeruli seen in a good core of renal cortex. The 1980s, however, saw a retreat from the paradigm of the primary role of infection, and emphasis was placed on scarring as a result of reflux and the progressive nature of the glomerular lesion associated with glomerular hypertension (or hyperfiltration), so-called reflux nephropathy. Renal Scarring in Adults A practical clinical problem is the differential diagnosis of scarred, asymmetric kidneys. With older patients, the differential diagnosis of scarred or "lumpy bumpy" kidneys widens. Often attributed to analgesic nephropathy in the 1970s, this appearance now is often designated "reflux nephropathy. Missing papillae leave a round hole in the medulla (arrow) and give a clubbed appearance. There is gross scarring and distortion of the calyceal pattern of the right kidney, giving rise to clubbed appearance of the dilated calyces. With reflux, there is a predilection for scarring of the upper and lower poles; with papillary necrosis or analgesic nephropathy, changes are less predictable. The uniformly small shrunken kidney has relative preservation of the calyceal pattern. It can be familial, and the term hereditary renal aplasia is used by pediatricians. It is an autosomal dominant trait with incomplete penetrance and variable expression and can be associated with bilateral renal agenesis or severe dysplasia. The remaining kidney is usually hypertrophic, but it may be ectopic, malrotated, or hydronephrotic with a megaureter. The more severe the dysplasia of the remaining kidney, the earlier is the presentation. The ipsilateral testis and seminal tract are usually absent, and in 10% of cases, the adrenal gland is also missing. Girls can have an absent fallopian tube or ovary or malformation of the vagina or uterus.
Specifications/Details
The typical presentation is sudden impairment in renal function acne scars purchase cleocin gel 20 gm mastercard, associated with mild proteinuria (<1 g/day) and abnormal urinalysis, in a patient with flank pain, normal blood pressure, and no edema. Hematuria and pyuria are present in a little more than half of the patients, and although leukocyte casts are common, hematuria is almost never associated with red blood cell casts. Flank pain, reflecting distention of the renal capsule, is observed in about one third of the patients and can be the main complaint on hospital admission. Ultrasound usually discloses an increased cortical echogenicity (comparable to or higher than that of the liver). Extrarenal symptoms consistent with a hypersensitivity reaction are occasionally observed, including low-grade fever, maculopapular rash. Most have been observed either after readministration of rifampin or several months after intermittent administration of the drug. Renal failure is usually associated with the sudden onset of fever, gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain), and myalgias. It may also be associated with hemolysis, thrombocytopenia, and less frequently hepatitis. Renal biopsy typically discloses tubular injury in addition to interstitial inflammatory infiltrates. Although circulating anti-rifampin antibodies are usually found in these patients, immunofluorescence staining of renal biopsy specimens has been negative in most cases, suggesting that cell-mediated immunity plays a key role in the induction of the nephritis. It was almost never associated with extrarenal symptoms or with anti-rifampin antibodies, and renal biopsy specimens showed severe interstitial infiltrates but few tubular lesions. There is also some experimental evidence that in the setting of renal impairment, allopurinol may precipitate as microcrystals or crystals and cause direct nephrotoxicity. The main difference is that extrarenal symptoms are present in only about 10% of patients. These infiltrative lesions are often patchy, predominating in the deep cortex and in the outer medulla, but they can be diffuse in severe cases. They are composed mostly of T cells and monocytes-macrophages, but plasma cells, eosinophils, and a few neutrophilic granulocytes may also be present. On light microscopy, the characteristic feature is interstitial infiltration with mononuclear cells, with normal glomeruli. Some drugs can induce the formation of interstitial granulomas, which reflect a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. These granulomas are usually sparse and non-necrotic, with few giant cells, and are associated with nongranulomatous interstitial infiltrates. Interstitial infiltrates are always associated with an interstitial edema, which is responsible for separating the tubules. These tubular lesions usually predominate where the inflammatory infiltrates are most extensive. Tubulointerstitial lesions are not associated with vascular or glomerular lesions. Nevertheless, staining of the tubular or capsular basement membrane for IgG or complement may occasionally be seen by immunofluorescence; the staining pattern is either granular or linear.
Syndromes
- If the bite is on the hand or fingers, call the doctor right away.
- Asthma
- If digital stimulation does not produce a bowel movement within 20 minutes, repeat the procedure.
- Remove and "lift" some of the fat tissue underneath the skin (called the SMAS layer; this is the main lifting part of the facelift)
- Is it worse when breathing deeply?
- Weak immune system (such as patients with AIDS, cancer, or an organ transplant; receiving chemotherapy or radiation therapy; or taking corticosteroid pills every day)
- If you have an important event scheduled, plan to arrive 2 or 3 days in advance. This will give you time to recover from jet lag.
- Chest x-ray, if the health care provider suspects pneumonia
- If necessary, perform first aid for eye injuries or convulsion first aid.
- Frothy stools
In health acne 911 purchase cleocin gel 20 gm visa, a tension exists between the normal immune response to foreign antigen and tolerance, which is the cellular process that prevents an immune response to self antigen. Tolerance develops because self-reactive T and B cells are clonally deleted during fetal and neonatal life, although small numbers survive outside the thymus or bone marrow, respectively. Under certain conditions, these peripheral self-reactive cells can be stimulated to generate a cellular and humoral response to a self antigen. These cells are decreased in patients with Goodpasture disease at presentation and may play a role in the loss of tolerance. Immune deposits with direct access to the circulation (subendothelial and basement membrane locations) are usually associated with leukocyte accumulation. Mesangial deposits elicit an intermediate response, whereas immune deposits in the subepithelial space generally are not associated with inflammatory cells. With acute injury, the predominant infiltrating cells are neutrophils, platelets, and monocytes, and in chronic injury, the predominant cells are monocyte/macrophages and T cells. The primary mechanism for attracting these cells is the secretion of chemokines and the expression of leukocyte adhesion molecules by local endothelial and resident cells; local release of complement activation fragments (C5a) is also important. Although neutrophils are common with immune complex disease, cell-mediated immunity is important in some glomerular diseases. For example, T cells likely have a role in crescentic nephritis, becoming sensitized to endogenous or exogenous antigen and then recruiting macrophages that mediate crescent formation. Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Fibrosis Intrinsic glomerular cells (epithelial, mesangial, and endothelial) are also activated in various glomerular diseases. Mesangial cells can become myofibroblast-like cells that proliferate and produce excessive extracellular matrix. Endothelial cells produce nitric oxide and other anti-inflammatory proteins, and injury to this cell population can result in the expression of leukocyte adhesion molecules and activation of the coagulation system. Podocytes are terminally differentiated cells; injury may not only result in proteinuria (see earlier) but when associated with apoptosis, may also result in glomerulosclerosis. Crescent formation represents a severe cellular response and is initiated by cytokine-driven proliferation, particularly of the parietal epithelial cells. Glomerular scarring is characterized by proliferation of mesangial cells with loss (apoptosis) of endothelial cells and podocytes. Tubulointerstitial fibrosis also accompanies progressive glomerular disease and correlates with both renal function and prognosis. Proteinuria has been shown to activate tubular cells and induce toxicity, either directly or through the generation of oxidants (from iron proteins excreted in urine) or from complement activation, which can be shown in proteinuric urine. Tubulointerstitial ischemia after loss of glomerular and peritubular capillaries may also drive fibrosis. Finally, loss of renal function may result from leakage of plasma ultrafiltrate into the peritubular space, resulting in a scarring response (misdirected filtration), or stenosis/occlusion of the opening of the proximal tubule from Bowman space, resulting in nonfunctional (atubular) glomeruli. A detailed discussion of current mechanisms involved in glomerulosclerosis is presented in Chapter 79. Breaks in Bowman capsule secondary to the periglomerular inflammation also occur, allowing the entrance of more inflammatory cells as well as fibroblasts.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: p.o.

Tags: cleocin gel 20 gm order with visa, purchase 20 gm cleocin gel visa, purchase 20 gm cleocin gel fast delivery, purchase cleocin gel 20 gm line
Customer Reviews
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Cleocin Gel
Irmak, 47 years: Treatment Pathology the morphologic features of the kidney in cystinosis vary with the stage.
Taklar, 27 years: In selected patients, assessment of the urine potassiumcreatinine ratio in a random urine specimen may be used, with potassium excretion less than 20 to 30 mmol/g creatinine suggesting inadequate renal excretion in the patient with hyperkalemia.
Jens, 59 years: The normal kidney possesses a remarkable ability to excrete potassium, so chronic hyperkalemia is difficult to produce unless renal potassium secretion is impaired.