Only $0.18 per item
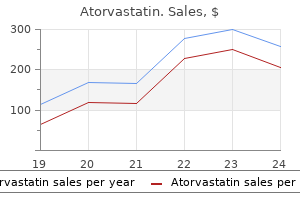
Atorvastatin dosages: 40 mg, 20 mg, 10 mg, 5 mg
Atorvastatin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 240 pills
In stock: 810
8 of 10
Votes: 41 votes
Total customer reviews: 41
Description
Hasegawa Y cholesterol levels when breastfeeding 20 mg atorvastatin with mastercard, Sakamoto N, Gotoh K: Relationship of ultrasonic and histologic findings in benign prostatic hyperplasia. The National Institutes of Health classification of prostatitis syndromes provides a useful conceptual framework. For example, acquired prostate cysts and calcification are typically asymptomatic, whereas prostatitis ranges from incidentally detected asymptomatic conditions to symptomatic cases. Other treatments, including both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic approaches, have been assessed as potential treatments for chronic prostatitis and pelvic pain syndromes. Acute bacterial prostatitis is most commonly caused by aerobic gram-negative rods, in particular Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas species. Bacteria may ascend to the prostate by reflux of infected urine into the prostatic duct, by lymphatic or hematogenous dissemination, or during interventions such as prostatic biopsy. Acute bacterial prostatitis is rare and is seen in less than 5% of patients with prostatitis. Acute bacterial prostatitis usually manifests as an acute illness with fever, chills, lower back and perineal pain, urinary frequency and urgency, and dysuria. The diagnosis of acute bacterial prostatitis is based primarily on clinical findings, in association with positive results of urinalysis and urine culture. In acute infection, the prostate enlarges secondary to infection and inflammation. Radiologic examinations usually are not required, unless severe infection and/or abscess is suspected. In acute prostatitis, the gland may appear normal or focally or diffusely enlarged. T1-weighted imaging is nonspecific owing to limited delineation of the internal structure of the prostate. On postcontrast T1-weighted images, the areas of inflammation enhance with gadolinium. Other ultrasound features of prostatitis include dilatation of the periprostatic venous plexus, elongated seminal vesicles, and thickening of the inner septa. Radiologic imaging is rarely required and only in the instance when severe infection and/or abscess is suspected. The diagnosis of acute bacterial prostatitis is based primarily on clinical findings, in association with positive results on urinalysis and urine culture. Prostatitis cannot be definitively differentiated from prostate cancer by imaging alone. Radiologic or surgical interventions are usually not required for acute prostatitis unless complicated by abscess formation.
Spinach. Atorvastatin.
- Dosing considerations for Spinach.
- Gastrointestinal complaints, fatigue, and stimulating growth in children.
- What is Spinach?
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Spinach work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96382
Alvestrand A cholesterol index chart atorvastatin 20 mg with amex, Wahren J, Smith D, et al: Insulin-mediated potassium uptake is normal in uremic and healthy subjects. De Wolf A, Frenette L, Kang Y, et al: Insulin decreases the serum potassium concentration during the anhepatic stage of liver transplantation. Mandelberg A, et al: Salbutamol metered-dose inhaler with spacer for hyperkalemia: how fast Blumberg A, Weidmann P, Ferrari P: Effect of prolonged bicarbonate administration on plasma potassium in terminal renal failure. Allon M, Shanklin N: Effect of bicarbonate administration on plasma potassium in dialysis patients: interactions with insulin and albuterol. Furuya R, Kumagai H, Sakao T, et al: Potassium-lowering effect of mineralocorticoid therapy in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Emmett M, et al: Effect of three laxatives and a cation exchange resin on fecal sodium and potassium excretion. Gruy-Kapral C, et al: Effect of single dose resin-cathartic therapy on serum potassium concentration in patients with end-stage renal disease. De Nicola L, et al: Effect of dialysate sodium concentration on interdialytic increase of potassium. Allon M: Medical and dialytic management of hyperkalemia in hemodialysis patients. Wizemann V, Kramer W, Funke T, et al: Dialysis-induced cardiac arrhythmias: fact or fiction Importance of preexisting cardiac disease in the induction of arrhythmias during renal replacement therapy. Redaelli B, et al: Effect of a new model of hemodialysis potassium removal on the control of ventricular arrhythmias. Santoro A, et al: Patients with complex arrhythmias during and after haemodialysis suffer from different regimens of potassium removal. Goutorbe P, et al: Intestinal necrosis associated with orally administered calcium polystyrene sulfonate without sorbitol. Amaya F, Fukui M, Tsuruta H, et al: Simulation of potassium extraction by continuous haemodiafiltration. Allon M, Shanklin N: Effect of albuterol treatment on subsequent dialytic potassium removal. This homeostatic system is modulated by dietary and environmental factors, including vitamins, hormones, medications, and mobility. Disorders of extracellular calcium homeostasis may be regarded as perturbations of this homeostatic system, either at the level of the genes controlling this system.
Specifications/Details
Patients with underlying pulmonary disease may not respond to metabolic acidosis with an appropriate ventilatory response because of insufficient respiratory reserve cholesterol levels elevated generic atorvastatin 40 mg otc. Such imposition of respiratory acidosis on metabolic acidosis can lead to severe acidemia and a poor outcome. When metabolic acidosis and metabolic alkalosis coexist in the same patient, the pH may be normal or near normal. A diabetic patient with ketoacidosis may have renal dysfunction resulting in simultaneous metabolic acidosis. Patients who have ingested an overdose of drug combinations such as sedatives and salicylates may have mixed disturbances as a result of the acid-base response to the individual drugs Table 17. The serum bicarbonate concentration usually does not increase above 38 mEq/L, however. The clinical features of respiratory acidosis vary according to the severity, duration, underlying disease, and presence or absence of accompanying hypoxemia. A rapid increase in Paco2 may result in anxiety, dyspnea, confusion, psychosis, and hallucinations and may progress to coma. Lesser degrees of dysfunction in chronic hypercapnia include sleep disturbances, loss of memory, daytime somnolence, and personality changes. Coordination may be impaired, and motor disturbances such as tremor, myoclonic jerks, and asterixis may develop. A reduction in ventilatory drive from depression of the respiratory center by a variety of drugs, injury, or disease can produce respiratory acidosis. Acutely, this may occur with general anesthetics, sedatives, narcotics, alcohol, and head trauma. Chronic causes of respiratory center depression include sedatives, alcohol, intracranial tumors, and the syndromes of sleep-disordered breathing, including the primary alveolar and obesity-hypoventilation syndromes. Neuromuscular disorders involving abnormalities or disease in the motor neurons, neuromuscular junction, and skeletal muscle can cause hypoventilation. Although a number of diseases should be considered in the differential diagnosis, drugs and electrolyte disorders should always be ruled out. Mechanical ventilation may result in respiratory acidosis when not properly adjusted and supervised or when complicated by barotrauma or displacement of the endotracheal tube. This occurs if carbon dioxide production suddenly rises (because of fever, agitation, sepsis, or overfeeding) or if alveolar ventilation falls because of worsening pulmonary function. High levels of positive end-expiratory pressure in the presence of reduced cardiac output may cause hypercapnia as a result of large increases in alveolar dead space. Permissive hypercapnia may be used because lower tidal volumes may reduce the incidence of the barotrauma associated with high airway pressures and peak airway pressures in mechanically ventilated patients with respiratory distress syndrome. The resulting hypercapnia, which is secondary to the attempt to limit airway pressures, causes the arterial pH to decline, and the degree of acidemia may be evident.
Syndromes
- Fainting or feeling light-headed
- Skin sores (ulcers)
- Liver disease with jaundice
- Problems keeping saliva in the mouth
- Be very tired
- Eyes, ears, nose, throat, and mouth
- In joints such as the shoulder
- Reducing or avoiding caffeine, certain cold medicines, and stimulants
- Malabsorption syndrome
The major cause is loss of magnesium in the cutaneous exudate cholesterol values mmol trusted 20 mg atorvastatin, which can exceed 1 g/ day. Hypomagnesemia is common in patients with diabetes mellitus, and has been reported to occur in 13. The latter could, in turn, be caused by glomerular hyperfiltration, osmotic diuresis, or decreased thick ascending limb and distal tubule magnesium reabsorption caused by functional insulin deficiency. Development of magnesium deficiency due to dietary deficiency in normal individuals is unusual because almost all foods contain significant amounts of magnesium, and renal adaptation to conserve magnesium is very efficient. Thus, magnesium deficiency of nutritional origin is observed primarily in two clinical settings-alcoholism and parenteral feeding. In chronic alcoholics, the intake of ethanol substitutes for the intake of important nutrients. The severity of hypomagnesemia in patients with malabsorption syndrome correlates with the fecal fat excretion rate and, in rare patients, reduction of dietary fat intake alone, which reduces steatorrhea, can correct the hypomagnesemia. Previous intestinal resection, particularly of the distal part of the small intestine, is also an important cause of magnesium malabsorption. Increased urine output from any cause is often accompanied by increased renal losses of magnesium. Renal magnesium wasting occurs with osmotic diuresis-for example, in hyperglycemic crises in diabetics. In such cases, it is likely that residual tubule reabsorptive defects persisting from the primary renal injury play as important a role as polyuria itself in inducing renal magnesium wasting. In the proximal tubule, magnesium reabsorption is passive and driven by the reabsorption of sodium and water in this segment. Extracellular volume expansion, which decreases proximal sodium and water reabsorption, also increases urinary magnesium excretion. Thus, chronic therapy with magnesium-free parenteral fluids, crystalloid or hyperalimentation,248 can cause renal magnesium wasting, as can hyperaldosteronism. Hypomagnesemia is, therefore, a frequent finding in patients receiving chronic loop diuretic therapy. The incidence of hypomagnesemia increases with increasing duration of therapy, reaching almost 50% in patients treated for longer than 6 months. Cisplatin, a widely used chemotherapeutic agent for solid tumors, frequently causes renal magnesium wasting. Aminoglycosides cause a syndrome of renal magnesium and potassium wasting with hypomagnesemia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and tetany. In addition, no correlation was found between the occurrence of aminoglycoside-induced acute tubular necrosis and hypomagnesemia. Magnesium wasting persists after cessation of the aminoglycoside, often for several months. All aminoglycosides in clinical use have been implicated, including gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin, as well as neomycin when administered topically for extensive burn injuries.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: p.r.n.
Tags: buy 40 mg atorvastatin with amex, generic atorvastatin 20 mg with mastercard, discount atorvastatin 40 mg free shipping, buy 5 mg atorvastatin with visa
Customer Reviews
Koraz, 34 years: The urinary phosphate excretion can drop to undetectable levels, indicating maximal urinary Pi reabsorption. Examples of histone modifications include phosphorylation, ubiquitinylation, sumoylation, acetylation, and methylation.
Diego, 49 years: Rarely, laparoscopic surgery may be required in persistently symptomatic segmental omental infarction. C, At 8 weeks, showing the fetal cortex and early permanent cortex beginning to encapsulate the medulla.
Aidan, 40 years: Common causative organisms are Neisseria gonorrhoeae and nongonococcal organisms, of which Chlamydia trachomatis is the most common. Although most of these cells cease to express renin in the adult, they appear to reexpress renin in stress conditions and are recruited to the afferent arteriole.
Mamuk, 27 years: Key Points Pyelonephritis · Pyelonephritis is infection of the renal pelvis, tubules, and interstitium. Saito T, Ishikawa S, Ando F, et al: Exaggerated urinary excretion of aquaporin 2 in the pathologic state of impaired water excretion dependent upon arginine vasopressin.
Amul, 35 years: Nevertheless, the local P continues to exceed the opposing throughout the length of the capillary bed in several tissues; thus, filtration occurs along its entire length. Labetalol, a broadly reactive sympathetic blocker, is a particularly common cause of hyperkalemia in susceptible patients.
Charles, 65 years: The endoderm of the primordial gut gives rise to the epithelial lining of the alimentary tract, except for the cranial and caudal parts, which are derived from ectoderm of the stomodeum and cloacal membrane, respectively. However, there are nests of adult stem cells in many other tissues, including those that have been previously considered nonregenerative, such as the central nervous system and retina.
Enzo, 44 years: Unfortunately, calcium status will be incorrectly predicted by this formula in 20% to 30% of subjects,10 and the agreement between corrected and free calcium is only fair. The septum secundum forms an incomplete partition between the atria; consequently, a foramen ovale forms.