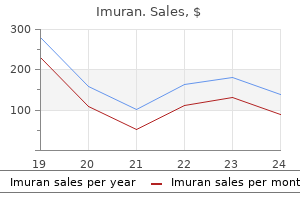
Only $0.72 per item
Imuran dosages: 50 mg
Imuran packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 843
9 of 10
Votes: 268 votes
Total customer reviews: 268
Description
Separated thymic tissue is often found scattered around the gland muscle relaxant use buy imuran 50 mg mastercard, and ectopic thymic rests are sometimes discovered in unusual mediastinal locations. Small accessory nodules may occur in the neck, representing separated portions, detached during embryological descent, and sometimes reaching more superiorly than the thyroid cartilage. Capsular tissue may have adhesions to the fibrous pericardium, which is thinner superiorly and may either easily tear or require a limited pericardotomy during thymectomy. Relations the thymus is largest in the early part of life, particularly around puberty, and persists actively into old age despite considerable fibrofatty degeneration that sometimes hides the existence of persistent thymic tissue. The greater part of the thymus lies in the superior and anterior mediastina; the inferior aspect of the thymus reaches the level of the fourth costal cartilages. As no definite hilum exists, the arterial branches either travel along the interlobar septa before entering the thymus at the junction of the cortex and medulla, or they reach the thymic tissue directly through the capsule. Trachea Cervical extensions of thymus Carotid arteries (low division) Veins Thymus, left lobe Thymus, right lobe Right lung Thymic veins drain to the left brachiocephalic, internal thoracic and inferior thyroid veins, and occasionally directly into the superior vena cava. One or more veins often emerge medially from each lobe of the thymus to form a common trunk opening into the left brachiocephalic vein and require careful ligation during thymectomy. Efferent lymphatics arise from the medulla and corticomedullary junction, drain through the extravascular spaces, accompany the supplying arteries and veins, and end in the brachiocephalic, tracheobronchial and parasternal nodes. Branches from the phrenic and descending cervical nerves (inferior roots of the ansa cervicalis) are distributed mainly to the capsule. The two lobes are innervated separately through their dorsal, lateral and medial aspects. During development and before its descent into the thorax, the thymus is innervated by the vagi in the neck. After its descent, the thymus receives a sympathetic innervation via fibres that travel along the vessels; postganglionic sympathetic terminations branch radially and form a plexus with the vagal fibres at the corticomedullary junction. Many of the autonomic nerves are doubtless vasomotor, but other terminal branches (at least in rodents) ramify among the cells of the thymus, particularly the medulla, suggesting that they may have other roles. The medulla contains a number of different types of non-lymphoid cells, including cells positive for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and acetylcholinesterase; large non-myoid cells; and cells containing oxytocin, vasopressin and neurophysin, of possible neural crest origin. These steps involve intimate interactions between thymocytes, mainly epithelial and antigen-presenting cells and chemical factors in the thymic environment. The thymus is also part of the neuroimmunological and neuroendocrine axes of the body, influenced by and influencing the products of these axes. Its activity therefore varies throughout life under the influence of different physiological states, disease conditions and chemical insults, such as hormones, drugs and pollutants.
Tinospora (Tinospora Cordifolia). Imuran.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Tinospora Cordifolia?
- How does Tinospora Cordifolia work?
- Dosing considerations for Tinospora Cordifolia.
- What other names is Tinospora Cordifolia known by?
- Diabetes, high cholesterol, upset stomach, gout, cancer including lymphoma, rheumatoid arthritis, liver disease, stomach ulcer, fever, gonorrhea, syphilis, and to counteract a suppressed immune system.
- Allergies (Hayfever).
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97101
The latter two components separate those parts of the primary heart tube that are committed to the right and left ventricles muscle relaxant 5658 imuran 50 mg order on line, as opposed to the ballooned apical ventricular components. Inappropriate formation and connection of the cushions with the muscular ventricular septum underscores deficiencies of the definitive ventricular septum; such lesions account for about two-thirds of all cardiac septal defects. Separation between the right and left ventricles is initially heralded by the appearance of a caudal crescentic ridge within the ventricular loop. The trabeculated parts of the ventricles contain less extracellular matrix than the walls of the primary heart tube, and it is these parts of the chambers that expand on each side of the ridge that remains between them. The more apical parts are added concomitant with enlargement of the chambers, as if they were expanding like balloons. The impression can be gained that the dorsal and ventral horns of the ventricular septum grow along the ventricular walls, meeting and fusing with the right extremities of the dorsal and ventral cushions of the atrioventricular canal. In reality, the crest of the septum marks the position of the original primary heart tube and becomes the atrioventricular bundle. The septum has a free, sickle-shaped margin that, together with the fused caudal surface of the endocardial cushions, bounds an ovoid foramen. Previously, this foramen has erroneously been termed the interventricular, or bulboventricular foramen; it is no more than a locus within the cavity of the primary heart tube. The apical trabecular components of the ventricles balloon from the ventral side of the primary heart tube. At the dorsal side, or the inner curvature, there is no chamber myocardium, only the smooth walls of the primary heart tube. Therefore, from the outset of the process, the forming apical parts of the ventricles are separated by a muscular septum. The foramen marked caudally by the crest of the ventricular septum provides the initial inlet to the developing right ventricle, and the outlet for the developing left ventricle. Completion of ventricular septation requires division of this primary foramen, rather than its closure. Use of inappropriate terminology means that the entire region upstream relative to the foramen has previously been called the primitive ventricle, the entire downstream region the bulbus, and the junction between them the bulboventricular junction. In the account presented here, the area is termed the primary junction, initially marked by a distinct notch on the outside of the heart, and inside by the corresponding ridge of the developing ventricular septum. The ridge is positioned between the atrioventricular orifice, which is initially a common structure, and the caudal part of the forming right ventricle. Septation of the ventricles After the looping of the heart tube, it is easy to gain the impression that the atrioventricular canal communicates exclusively with the developing left ventricle, while the outflow tract is supported exclusively by the developing right ventricle. A, A frontal view of the heart at stage 13, with the outflow tract reflected to the right. Lines show the level of transverse sections of the atrioventricular cushions and outflow tract. Note that blood from both atria passes through the embryonic interventricular foramen at this stage.
Specifications/Details
Internally muscle relaxant liquid form imuran 50 mg buy visa, the ventricles are separated by the septum; its mural margins correspond to the anterior and inferior (diaphragmatic) interventricular grooves. The anterior groove, seen on the sternocostal cardiac surface, is near and almost parallel to the left ventricular obtuse margin. On the diaphragmatic surface, the groove is closer to the midpoint of the ventricular mass. The interventricular grooves extend from the atrioventricular groove to the apical notch on the acute margin, the latter a little to the right of the true cardiac apex. It faces posteriorly and to Heart the right, separated from the thoracic vertebrae (fifth to eighth in the recumbent, sixth to ninth in the erect posture) by the pericardium, right pulmonary veins, oesophagus and aorta. It extends superiorly to the bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk and inferiorly to the posterior part of the atrioventricular groove, which contains the coronary sinus and coronary arterial branches. It is limited to the right and left by the rounded surfaces of the corresponding atria, separated by the shallow interatrial groove. The point of junction of the atrioventricular, interatrial and posterior (inferior) interventricular grooves is termed the cardiac crux. Two pulmonary veins on each side open into the left atrial part of the base, whereas the superior and the inferior venae cavae open into the upper and lower parts of the right atrial basal region. This description of the anatomical base reflects the usual position of the heart in the thorax. Such descriptions, while less than perfect anatomically, will almost certainly persist. Only a small part of the left atrial appendage projects forwards to the left of the pulmonary trunk. Of the ventricular region, about one-third is made up by the left and two-thirds by the right ventricle. The site of the septum between them is indicated by the anterior interventricular groove. The sternocostal surface is separated by the pericardium from the body of the sternum, the sternocostal muscles and the third to sixth costal cartilages. Because of the bulge of the heart to the left, more of this surface is behind the left costal cartilages than the right. It is also covered by the pleural membranes and the thin anterior edges of the lungs, except for a triangular area at the cardiac incisure of the left lung. The lungs and their pleural coverings are variable in their degree of cardiac overlap. It is formed by the ventricles (chiefly the left) and rests mainly on the central tendon but also, apically, on a small area of the left muscular part of the diaphragm. It is separated from the anatomical base by the atrioventricular groove, and is traversed obliquely by the posterior (inferior) interventricular groove. Left surface of the heart Facing posterosuperiorly to the left, the left surface consists almost entirely of the obtuse margin of the left ventricle, but a small part of the left atrium and its left atrial appendage contribute superiorly. Convex and widest superiorly, where it is crossed by the atrioventricular groove, it narrows to the cardiac apex.
Syndromes
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Are coughing up dark mucus.
- Frequent doctor visits to make sure you and your baby are doing well
- Tuberculin skin test
- Dried fruit
- Kneecap cartilage that has been damaged may be removed.
A more recent classification of upper limb anomalies muscle relaxant amazon discount 50 mg imuran overnight delivery, based on developmental molecular biology and pathogenetics, clearly defines all terms used to describe anomalous structure and provides a comprehensive and consistent terminology for the range of anomalies (Oberg et al 2010, Tonkin et al 2013, Goldfarb 2015). It occurs because of failure to remove cells between the digit rays during stages 1923. Clinodactyly is a congenital condition in which the little finger is curved towards the ring finger. Camptodactyly is a congenital condition in which the little finger, and sometimes the ring finger, are held in a fixed, flexed position. Symphalangism is a rare congenital disorder in which there is fusion of the interphalangeal joints. The affected finger is stiff, skin creases are absent over the affected joint, there is minimal joint space, and sometimes the digit is shorter than normal. Several different types of brachydactyly, shortening of the digits, can be recognized according to which digits and which parts of these digits are affected. The genetic basis of different types of brachydactyly has now been determined, which is particularly gratifying because brachydactyly was the first condition in humans to be recognized as a dominant Mendelian condition (Gao and He 2004). The basis of limb reductions seen in infants whose mothers took thalidomide during their pregnancy seems likely to be due to death of mesenchyme cells in the early limb bud, causing phocomelia. A source that includes articles on embryology, growth and congenital anomalies of the hand. A source that sets out details of an accepted classification for congenital limb malformations. Valasek P, Theis S, Krejci E et al 2010 Somitic origin of the medial border of the mammalian scapula and its homology to the avian scapula blade. Ito T, Ando H, Suzuki T et al 2010 Identification of a primary target of thalidomide teratogenicity. This paper considers the development of the transition zones between the head and neck, the back and the pectoral girdle. Establishes the avian scapular blade and medial border of the mammalian scapula as homologous structures that share the same developmental origin. Valasek P, Theis S, DeLaureir A et al 2011 Cellular and molecular investigations into the development of the pectoral girdle. Provides evidence that the formation of the muscles of the proximal limb occurs through two distinct mechanisms. The combined motion of the shoulder and elbow brings objects in the hand into the visual field, while the great range of the shoulder and pectoral girdle enable reaching into a wide external environment. Oculospinal afferents appear to be the most important modulators of shoulder joint stability necessary for reaching. An object is first reached and then grasped (increasing both superficial and deep peripheral afferent inputs that enhance proximal shoulder girdle stability (Alizadehkhaiyat et al 2011)), before being retrieved into the visual field. Closepacking occurs through a lesser, more specific, range of motion in the elbow; the flexed elbow with a supinated forearm is the position for carrying the greatest load with the least energy expenditure or the greatest resistance to fatigue.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: p.r.n.

Tags: buy imuran 50 mg without a prescription, discount 50 mg imuran, imuran 50 mg on line, cheap imuran 50 mg buy on line
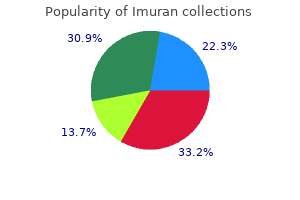
Customer Reviews
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Imuran
Lukar, 60 years: The right border of the liver is curved to the right and joins the upper and lower right limits. The midgut extends between the intestinal portals and, in the early embryo, is in wide communication with the yolk sac. Fibrocartilage covers the articular surfaces and also unites the costal cartilages and the sternum in those joints where cavities are absent.
Sanuyem, 59 years: It carries the bile duct, portal vein and hepatic artery, and its hepatic end is reflected around the porta hepatis. An average adult heart is 12 cm from base to apex, 89 cm at its broadest transverse diameter and 6 cm anteroposteriorly. Its medial and dorsal surfaces are confluent, and marked distally by the attachment of the ulnar collateral ligament, but smooth proximally to receive the articular disc of the distal radio-ulnar joint in full adduction.
Jared, 33 years: Inferiorly, the circular muscle is continuous with the oblique layer of muscle fibres in the stomach wall. The standard approach is via an incision from the anterior axillary line, which curves about 4 cm below the tip of the scapula and then vertically between the posterior midline and medial edge of the scapula. The left pulmonary artery sling is a congenital abnormality characterized by the left pulmonary artery arising from the right pulmonary artery, coursing over the right principal bronchus and heading posteriorly between the trachea and oesophagus.
Gorok, 64 years: In the early embryo, the connection between one pericardioperito neal canal and the other was directly across the ventral surface of the cranial midgut, immediately caudal to the developing primitive ventral mesogastrium. Pathological states become manifest by abnormal secretion, impaired absorption, disordered gastrointestinal motility and pain. In such cases, the posterior intercostal artery may be accessed by placing a catheter in the thoracic aorta, usually by puncturing the femoral artery in the groin.