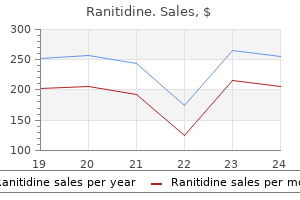
Only $0.26 per item
Ranitidine dosages: 300 mg, 150 mg
Ranitidine packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 605
8 of 10
Votes: 128 votes
Total customer reviews: 128
Description
Many sperm cluster around the oocyte and attempt to penetrate the granulosa cells (figure 18 gastritis y colitis 150 mg ranitidine purchase free shipping. The acrosomes of the sperm release enzymes that dissolve the "glue" holding granulosa cells Fertilization After semen is deposited in the vagina, sperm begin their long journey into the uterus and on into the uterine tubes. Sperm inherently swim against the slight current of fluid that flows from the uterine tubes through the uterus and into the vagina, which helps to guide sperm towards the uterine tubes. It takes many sperm to disperse the granulosa cells, so that one sperm can eventually wriggle between them to contact the oocyte. The acrosome then releases a different enzyme that enables the sperm to penetrate the oocyte membrane and enter the oocyte. Once this happens, changes in the oocyte plasma membrane prevent other sperm from entering (figure 18. When a sperm enters the secondary oocyte, it triggers the second meiotic division, which forms the ovum and a second polar body. Then, the sperm nucleus and ovum nucleus unite in fertilization to form a zygote, the first cell of the infant-to-be. Most sperm remain viable in the female reproductive tract for about 72 hours, although some may be viable for up to five days. Therefore, fertilization is most likely to occur when sexual intercourse occurs from three days before ovulation to one day after ovulation. Located within the blastocyst is the embryoblast or inner cell mass, a specialized group of cells from which the embryo later develops. The superficial wall of the blastocyst is called the trophoblast, which later will form the embryonic portion of the placenta. Digestive enzymes, released from the trophoblast, enable the blastocyst to penetrate into the endometrium, where it is soon covered by the superficial endometrium. This entire process is called implantation and is completed by the fourteenth day (figure 18. Clinical Insight Identical, or monozygotic, twins develop from a single zygote; this means that the twins possess identical genetic characteristics. The embryoblast of the blastocyst separates completely, usually by the end of the first week of embryonic development, and results in two embryos within separate amnion sacs yet sharing a common chorion and placenta. Fraternal, or dizygotic, twins develop from two zygotes: two different secondary oocytes are fertilized by different sperm. These twins do not possess identical genetic characteristics and develop within separate amnions and chorions. Each embryo develops its own placenta, though the placentas may fuse if they are located near each other within the uterus. Preembryonic Development Immediately after fertilization, the zygote begins to divide by mitotic cell division. These divisions occur so rapidly that maximum cellular growth between divisions is not possible, which results in increasingly smaller cells.
Nine Hooks (Alchemilla). Ranitidine.
- How does Alchemilla work?
- Is Alchemilla effective?
- Dosing considerations for Alchemilla.
- Diarrhea, skin conditions such as ulcers, eczema, and rashes, diabetes, menstrual irregularities, bleeding and wound healing, stomach disorders, muscle spasms, and others.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Alchemilla?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96644
With immediate fecal peritonitis source control gastritis diet bananas buy 150 mg ranitidine with amex, residual peritonitis rates are 41% [2]. A planned early repeat laparotomy is associated with a lower mortality rate versus an emergency laparotomy in response to an acutely sick patient (0% vs. Hence, early recognition and a low threshold for planned repeat laparotomy is necessary to minimize mortality; this should be done with surgeons in order to repair any bowel trauma. Presentation is similar to bowel trauma with abdominal pain, distension of the abdomen, vomiting, lack of bowel sounds, and constipation. Once more serious causes are excluded, management is by a nasogastric tube, intravenous rehydration, and attention to electrolyte imbalance to avoid hypokalemia (Chapter 56). An ileus is more likely if the patient has experienced prolonged starvation before or after surgery. Constipation the psychologic and physiologic stresses of surgery can cause reduced bowel motility, which can be aggravated by drugs such as opiates. Before a diagnosis of constipation is made, other more serious causes such as bowel trauma should be excluded. Constipation is relieved by increased patient mobility, oral hydration and, if necessary, enemas or laxatives. Bladder or ureteric trauma Bladder trauma can present with a pseudosac (swollen bladder on ultrasound with entrapped gas), hematuria, presence of urine in the abdominal or pelvic cavity, and postoperative anuria. With ureteric trauma, there can be flank pain, an ileus, distended abdomen, and pyrexia if there is concomitant sepsis. Management requires involving urologists as soon as the diagnosis is suspected or made, as prompt diagnosis and treatment is crucial in decreasing morbidity [3]. Management of bladder and ureteric injuries, including those diagnosed postoperatively, is discussed in Chapters 35 and 36, respectively. Urinary retention Urinary retention can be a complication of a bladder infection, trauma, or decreased bladder function after surgery. A bladder scan is the correct approach to diagnose retention; catheterization should not be used to diagnose retention. Once trauma has been excluded, treatment is with urinary catheter reinsertion to allow the bladder more time to rest before a further trial without catheter can be conducted. Urinary tract infection Urinary tract infections are common after surgery and if not treated promptly can cause pain and complications such as pyelonephritis. Pyelonephritis will have associated symptoms of loin pain, vomiting, and high pyrexia. A urine sample should be dipped for the presence of nitrates and appropriate antibiotics should be prescribed in accordance with local microbiology guidelines. If the urine dipstick is equivocal, a midstream urine sample should be sent for microscopy, culture and sensitivity before antibiotics are commenced.
Specifications/Details
Except for gamma globulins gastritis diet çùêòù order 150 mg ranitidine fast delivery, plasma proteins are produced by the liver and are released into the blood. Cholesterol occurs in the blood in combination with triglycerides and carrier proteins. Blood cholesterol levels result from a combination of heredity, diet, and exercise. A total blood cholesterol level less than 200 mg/dl (milligrams per deciliter) is a desirable goal. Whenever blood vessels are damaged, the loss of blood poses a considerable threat to homeostasis. Hemostasis is a positive-feedback mechanism initiated after vascular injury to stop or limit blood loss. There are three separate but interrelated processes involved in hemostasis: vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, and coagulation (figure 11. As platelets accumulate at the site of the damage, they secrete serotonin, a chemical that continues the contraction of the smooth muscles in the damaged vessel. Platelet Plug Formation Platelets normally do not stick to each other or to the wall of the blood vessel because the vessel wall contains several substances that repel platelets. However, when a vessel is damaged, the collagen in areolar connective tissue is exposed. Platelets are attracted to the site and adhere to the negatively charged collagen and to each other so that a cluster of platelets accumulates to plug the break (figure 11. This process is enhanced by the chemicals released from both the damaged blood vessel wall and platelets aggregated at the damaged site. The formation of a platelet plug may not seal off the damaged blood vessel but it sets the stage for coagulation. Vascular Spasm A vascular spasm, or constriction, of the blood vessel results from contraction of smooth muscle within the vessel wall at the damaged site (figure 11. Physical damage to the vessel causes the release of chemicals that initiate the spasm. The formation of a blood clot is a complex series of chemical reactions involving many substances. Blood contains both procoagulants, substances that promote clotting, and anticoagulants, substances that inhibit clotting. However, when a vessel is injured, the increase in procoagulant activity starts the clotting process. Clot formation is a complex process but it is completed within three minutes after a blood vessel has been damaged.
Syndromes
- Stroke
- Hole that develops through the entire wall of the stomach, small intestine, large bowel, or gallbladder (gastrointestinal perforation)
- Impaired judgment
- Do NOT give the person food or drink.
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases - www.niams.nih.gov/Health_Info/Psoriasis/default.asp
- Familial hypercholesterolemia
- Is there numbness or tingling with the weakness?
- Irritability
- Loss of muscle mass
- Trauma or injury to the chest and esophagus
Overall regulation of body temperature is controlled by the 5 gastritis shortness of breath 300 mg ranitidine order with amex, and the 6 plays a key role in conserving and dissipating heat. When body temperature falls below normal, the flow 7 of to the skin is decreased, which decreases heat loss from the skin surface. Shivering increases cellular respiration in skeletal muscles, which generates more 10. When body temperature rises above normal, blood flow to the skin is 11, which increases heat loss from the skin surface. If body temperature becomes extremely high, 12 are activated and begin to secrete 13 onto the surface of the skin. Why is the subcutaneous tissue especially good for rapid absorption of medications Label the diagram by placing the number of each structure by the correct label (some structures might match with more than one number). Bones of the Skeleton 1 2 Write the names of the labeled bones in the spaces provided. Label the diagram of the skull, anterior view, by placing the number of each structure in the space by the correct label. Nasal concha, inferior Nasal concha, middle Parietal bone Squamous suture Sphenoid (2 places) Temporal bone Vomer Zygomatic bone 448 Chapter 6 Study Guide c. Label the diagram of the skull, lateral view, by placing the number of each structure in the space by the correct label. Name the group of bones that provides protection for the 1) Brain 2) Heart and lungs Label the vertebra by placing the number of the structure in the space by the correct label. Its function is to support the upper articulates with the scapula at one end and at the other. Label these diagrams by placing the number of each structure in the space by the correct label. Label the diagrams by placing the number of each structure in the space by the correct label. Indicate whether each of the following is associated with the fibula (F) or tibia (T). Lateral malleolus Lateral condyle Articulates with femur Medial malleolus Medial condyle Articulates with talus 452 Chapter 6 Study Guide 8. Disorders of the Skeletal System Write the name of each disorder described in the space provided. What is this injury, and do you expect it to drastically alter the players ability to play soccer Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. Structure of Skeletal Muscle Write the terms that match the statements in the spaces at the right. The terminal bouton of an activated somatic motor 1) 1 into the 2 where it binds neuron releases 2) 3.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: p.r.n.
Tags: discount ranitidine 150 mg buy, 300 mg ranitidine order amex, cheap 300 mg ranitidine with amex, buy discount ranitidine 150 mg line
Customer Reviews
Navaras, 63 years: The larger cell is the secondary oocyte, and it contains nearly all of the cytoplasm that was present in the primary oocyte. The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, and organs, collectively called endocrine glands, that secrete hormones (chemical messengers) into the interstitial fluid.
Basir, 51 years: For each section of a nephron and the collecting duct, what substances are reabsorbed and secreted during the formation of the urine entering the minor calyx In females, it infects the vagina and may spread to the urethra, uterus, uterine tubes, and pelvic cavity.
Randall, 36 years: The ureter is mobilized off the pelvic sidewall peritoneum, from pelvic brim down to the level of the bladder. To add to the complexity of polygenic inheritance, each gene involved may possess a number of different alleles.