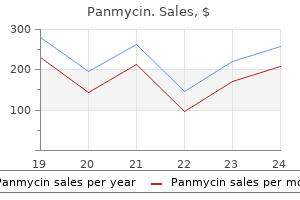
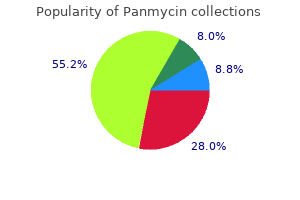
Only $0.54 per item
Panmycin dosages: 500 mg, 250 mg
Panmycin packs: 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 706
8 of 10
Votes: 46 votes
Total customer reviews: 46
Description
The A2 Ca2+ channel subunit, for example, is an auxiliary subunit up-regulated in neuropathic pain models virus hives panmycin 250 mg buy on-line. This is the binding site of the antineuropathic pain drugs gabapentin and pregabalin (Hendrich et al 2008, Taylor 2009). Yet another hint that the trafficking of ion channels and receptors may be a key substrate for chronic pain comes from genomic screens. Pain, particularly neuropathic pain, is highly variable from individual to individual even when the precipitating nerve injury or disease is the same. Useful information can be derived from genetic comparison of cohorts (animals or patients) that have and do not have pain. At their best, genetic studies analyze the entire genome in an unbiased manner, free of investigator preconceptions about what genes might be important. Remarkably, a considerable proportion of such studies, covering painful conditions ranging from migraine headache to neuropathy, have converged on polymorphisms in genes coding for auxiliary Ca2+ channel subunits, including auxiliary subunits related to protein trafficking. Polymorphisms in several of these genes are also implicated in epileptogenesis, a condition already allied with neuropathic pain on the grounds that anticonvulsant drugs often provide effective pain relief (Barclay et al 2001, de Vries et al 2009, Neely et al 2010, Nissenbaum et al 2010, Tselnicker et al 2010). These observations, which are unlikely to be just coincidental, focus attention on protein trafficking and distribution as a potentially productive avenue for future research. Current-Carrying Capacity of Ion Channels Already in Place Ion channels determine cell excitability by controlling the transmembrane flow of ionic currents. An increase in net flow through a fixed number of channels has much the same effect as an increase in the total number of channels present. Increased net flow can result from a higher probability of channels opening, extended channel open time, incomplete inactivation, or increased unitary channel conductance. Such changes in the intrinsic kinetics of ion channel behavior 885 represent a third process that can contribute to neuronal hyperexcitability. Evidence is accumulating that modulation of the currentcarrying capacity of voltage-gated channels might contribute to neuropathic pain. For example, cyclic adenosine monophosphatedependent phosphorylation of Na+ channels reduces Na+ current, wherease dephosphorylation returns it to normal (Li et al 1992, Gold et al 1998, Vijayaragavan et al 2004, Chahine et al 2005, Hudmon et al 2008). The ultimate test of the hypothesis, however, is its ability to explain the efficacy of known therapeutic agents and to predict new ones. Membrane Stabilization versus Synaptic Action Pain relieving drugs that suppress electrogenesis act through either membrane processes or synaptic processes. Examples of drugs that act on membrane excitability, but not synapses, are the local anesthetic lidocaine and the anticonvulsant carbamazepine. Drugs thought to act predominantly by a synaptic action include the -aminobutyric acid receptor ligands baclofen and midazolam.
Long Purples (Purple Loosestrife). Panmycin.
- What is Purple Loosestrife?
- How does Purple Loosestrife work?
- Diarrhea, intestinal problems, menstrual (period) complaints, inflammation, infection, varicose veins, bleeding gums, hemorrhoids, eczema, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Purple Loosestrife.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96403
Even in most of the trials with a negative outcome with respect to pain, a positive impact of gabapentin on improvement in sleep, mood, and quality of life was demonstrated infection precautions panmycin 250 mg sale. In the beginning of this century, gabapentin was used more frequently than any other anticonvulsant for chronic pain. This popularity was due to ease of administration, lack of need for monitoring, relatively low incidence of serious adverse events, and a perception of efficacy bolstered by evidence from placebo-controlled trials. When compared with other anticonvulsants, drugdrug interactions are not significant. The dose must be adjusted in patients with renal failure, but no adjustment is necessary in patients with hepatic disorders since it is not metabolized in the liver. The new drug combines generic gabapentin with a polymeric delivery system to provide extended release and is licensed to be given only as a once-daily dosing regimen (Thomas and Farquhar-Smith 2011). The proportion of patients with 30 and 50% or greater decreases in mean pain scores was greater in the pregabalin than in the placebo group (63 versus 25% and 50 versus 20%, P = 0. This 12-week, multicenter study involving either flexible-dose pregabalin, 150 to 600 mg/day (n = 70), or placebo (n = 67) constitutes one of the largest clinical studies on pain with spinal cord injury and clearly showed that in patients allowed to keep taking their existing stable pain medication, pregabalin was associated with a reduction in pain whatever the primary pain treatment was. The body of literature on both gabapentin and pregabalin suggests that they possess similar efficacy and tolerability. Some superiority of pregabalin, which is supposed to exert its pharmacological effects via the same mode of action as gabapentin, is attributed to its linear pharmacokinetics, twice-a-day dosing, and shorter titration phase to achieve an efficacious dose. The only data available come from some occasional reports from small and less-controlled studies. A recent publication on substitution of gabapentin therapy with pregabalin in an open-label assessment suggested that pregabalin could provide additional pain relief and increase in quality of life, at least in a group of patients with peripheral neuropathy (Toth 2010). Although the early pregabalin studies excluded gabapentin non-responders, this strategy has been abandoned recently, and all newer studies include patients who have shown no or limited response to gabapentin before study entry. In a recent review by Finnerup and colleagues (2010) in which the 12 published pregabalin trials up to that point were summarized, the response rate to pregabalin was calculated to be 39%, whereas 20% responded to placebo. However, the authors admitted that inclusion of still unpublished trials would change this relationship to 42% for pregabalin and 31% for placebo (Finnerup et al 2010). The most common adverse effects of carbamazepine are excessive sedation and ataxia. Regular monitoring of hematological and hepatic function is necessary, drugdrug interactions are common, and there is a rare but serious occurrence of irreversible aplastic anemia. Cognitive impairment, sedation, orthostatic hypotension, and sexual dysfunction are also common and poorly tolerated. Amitriptyline, the most studied drug of this class, has been found to be one of the medications that should be avoided in the elderly. Since the tricyclics have been generic for decades, no large studies have been conducted, as is now standard for any new drug that is being submitted to trials for approval, thus posing a difficulty in interpreting historical data from small single-center studies.

Specifications/Details
Fuchs and colleagues (LaBuda and Fuchs 2000) developed an important protocol to measure the aversive qualities of pain based on avoidance of a location that has been associated with the application of a stimulus to an inflamed or nerve-injured paw antibiotics for sinus infection over the counter 500 mg panmycin purchase fast delivery. This assay, the "place escape avoidance paradigm," provided significant mechanistic insight into the aversive nature of experimental neuropathic pain (LaBuda and Fuchs 2000). The animals are allowed unrestricted movement during the 30-minute testing paradigm. While the rats are in the dark chamber, mechanical stimuli (476-mN von Frey filament) are applied at 15-second intervals to the hindpaw ipsilateral to the injury or inflammation, and while the animal is in the light chamber, the stimulus is applied to the contralateral hindpaw (LaBuda and Fuchs 2000). The rats with either nerve injury or inflammation spent a significantly greater amount of time in the light chamber, thus suggesting avoidance of the chamber associated with hyperalgesia, whereas the control groups consisting of sham-operated or vehicle-injected rats spent an equivalent amount of time in each chamber (LaBuda and Fuchs 2000). Additionally, it was noted that although the rats would occasionally explore the dark chamber, they would leave before application of the next stimulus, which suggests that the rats would anticipate and avoid the stimulus applied to the hyperalgesic hindpaw (LaBuda and Fuchs 2000). Negative Reinforcement with Conditioned Place Preference the development of this approach (King et al 2009) was based on the knowledge that relief of pain is rewarding in humans (Seymour et al 2005). Pain has a strong emotional component as exemplified by its unpleasantness, and chronic pain produces an aversive state (Johansen et al 2001, Vierck et al 2008). The unpleasantness of pain serves as the "teaching signal" that forces avoidance of stimuli that can potentially produce damage to tissues (Price 2000, Johansen et al 2001, King et al 2009). For this reason, pairing pain relief with a context resulted in negative enforcement (King et al 2009) and led to the demonstration of "unmasking" of spontaneous experimental neuropathic pain. In this way, drugs that do not normally elicit reward do so in the presence of chronic pain. Two chambers separated by a neutral chamber had different visual and textural characteristics. After a period of preconditioning, a non-active control treatment is paired with one chamber and a treatment demonstrated to be effective for human neuropathic pain with Intrathecal Self-Administration in Experimental Pain States A novel methodology was developed in which intrathecal self-administration was used to determine the effectiveness of a treatment against spontaneous neuropathic pain. The 2-adrenergic agonist clonidine has been used successfully for the treatment of neuropathic pain clinically and has been effective against evoked measures of neuropathic pain in animal models (Xu et al 1992). Clonidine or -conotoxin delivered spinally to rats with nerve injury blocked the behavioral signs of tactile allodynia. Critically, these treatments produced place preference selectively in animals with nerve injury, thus indicating that the animals preferred the chamber where pain relief occurred (King et al 2009). These effects were demonstrated by interventions that are made outside the reward pathway. Additionally, this result suggested that injured nerve fibers can mediate pain in animals, consistent with observations in humans that aggravating a neuroma would produce pain whereas local anesthesia near the neuroma would reduce pain (Gracely et al 1992). Place preference was produced with a single pairing, a result suggesting that the peripheral nerve injury produces significant spontaneous pain. The sequence of innocuous and noxious exposure alternated daily and the novel objects were changed daily (Hummel et al 2008). Morphine-treated rats received the drug 45 minutes before the pain-pairing session. The day after the last conditioning session, the rats were allowed free access to both chambers, and time spent in each one was determined by an unbiased observer who reviewed video recordings of the sessions (Hummel et al 2008).
Syndromes
- You may want to visit a physical therapist before surgery to learn exercises that can help you recover.
- Skull x-ray
- Skin sores (boils)
- Morning sickness does not improve, despite trying home remedies.
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Nitrofurantoin
- Chew your food more thoroughly
- Blood loss (hemorrhage)
Myocardial infarction can also be "silent" in many patients, particularly in the elderly and those with cardiovascular disease or diabetes mellitus (Valensi et al 2011) antibiotic unasyn order panmycin 250 mg without a prescription. One explanation for painless myocardial ischemia is "neural stunning," whereby previous ischemic activity renders the sensory sympathetic fibers less sensitive (Pettersen et al 1995, Abe et al 1998). Another possibility is that cardiac afferents are normally rather unresponsive and sensitized only by pathology, more so in some than others (Malliani 1986). When myocardial ischemia is present, pain intensity cannot be used to distinguish between reversible myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction (Eriksson et al 1994). Approximately 20% of patients in whom coronary artery disease is suspected clinically are found to have normal to nearly normal coronary arteries at the time of angiography (Kemp et al 1986), and some proportion of these patients are said to have cardiac syndrome X (Shimokawa and Yasuda 2008, Cannon 2009, Lim et al 2009). Although the definition of this syndrome continues to evolve (Vermeltfoort et al 2010), it reasonably includes exertional angina pectoris accompanied by ischemia-like changes on the electrocardiogram or reversible perfusion deficits with stress testing despite normal findings on coronary arteriography. Patients with cardiac syndrome X are more likely to be women, particularly those who are post-menopausal (Kaski 2002) and have estrogen deficiency (Rosano et al 1995, Kaski 2006). Patients with cardiac syndrome X are more likely to report pain with mechanical or benign electrical stimulation of the heart, intracoronary injection of contrast media, and infusion of adenosine or dipyridamole (Shapiro et al 1988, Cannon et al 1990b, Lagerqvist et al 1992, Rosen et al 1994b, Pasceri et al 1998), and this sensitivity also occurs with esophageal stimulation (Cannon et al 1990a). Anxiety and panic disorder are often observed in patients with cardiac syndrome X (Bass et al 1983, Beitman et al 1989, Pasceri et al 1998, Rutledge et al 2001). Functional brain imaging reveals a level of central activation in syndrome X patients comparable to that observed in those with myocardial ischemia, but with characteristic activation of the insular cortex (Rosen and Camici 2000, Rosen et al 2002). Microvascular abnormalities as a result of coronary endothelial dysfunction appear to be an important component of cardiac syndrome 726 Section Five Clinical States/Viscera X (Hurst et al 2006). Long-term outcome studies of patients with cardiac syndrome X initially revealed little impact on survival but demonstrated how unresolved chest pain could impair lifestyle (Kaski et al 1995, Lichtlen et al 1995). However, more recent data recognize that coronary and cerebrovascular disease is more likely to develop in those with demonstrable endothelial dysfunction (Targonski et al 2003, Bugiardini et al 2004). Pericardium A large variety of idiopathic, inflammatory, neoplastic, congenital, metabolic, traumatic, rheumatological, iatrogenic, and infectious conditions, either systemic or specifically associated with the pericardium or adjacent organs, can lead to pain of pericardial origin (Spodick 2001). Pericardial pain can be severe, is often sudden in onset and substernal in location with radiation similar to that of myocardial ischemia but may also include the trapezius ridge, and can be sharp or dull in character. It worsens with inspiration and recumbency but improves with sitting and leaning forward. Auscultation may reveal a rub with components related to atrial systole, ventricular systole, and diastole. Pericardial fluid may render heart sounds more distant, and constriction may introduce a sound in early diastole.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: q._h.

Tags: order panmycin 500 mg with mastercard, panmycin 500 mg purchase visa, buy panmycin 500 mg visa, discount panmycin 500 mg visa
Customer Reviews
Mine-Boss, 40 years: Finally, episodic (Bahra et al 2001) and chronic (Matharu et al 2003a) migraine sufferers share the same area of activation in the dorsolateral pons on functional brain imaging.
Marlo, 52 years: The impact on working life is especially relevant for amputees who become handicapped at a young age.
Fabio, 63 years: The importance of careful clinical studies is highlighted by the fact that several important mechanisms underlying the pain in peripheral neuropathies have emerged from investigations of patients that 926 were not predicted by work on animal models of neuropathic pain.