Only $0.39 per item
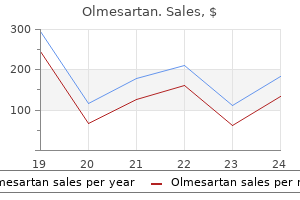
Olmesartan dosages: 40 mg, 20 mg, 10 mg
Olmesartan packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 666
8 of 10
Votes: 232 votes
Total customer reviews: 232
Description
Uyama M blood pressure chart pulse olmesartan 40 mg purchase overnight delivery, Takahashi K, Kozaki J, et al: Uveal effusion syndrome: clinical features, surgical treatment, histologic examination of the sclera, and pathophysiology. Oliver M, Uchenick D: Bilateral exudative retinal detachment in eclampsia without hypertensive retinopathy. It is probable that local cellular production of growth factors is responsible for these mitogenic effects. The evidence for growth control by local autocrine or paracrine mechanisms is well established in analogous biologic systems such as wound healing, in which. Presumably, disruption of the bloodocular barrier is a general stimulus that evokes cellular production of growth factors. The revised system of diagnosis and classification is further described in the remainder of this section. It is for this reason that vitreous contraction can be severe, despite its relative hypocellularity. These membranes subsequently become opaque and produce several characteristic patterns of contraction (grade C), in either the posterior or the anterior retina. The retina is contracted in an anteroposterior direction, which flattens its normally bullous convex curvature, and in a circumferential direction, which creates a series of radial folds in the anterior retina. Traction is exerted on the remainder of the retina, pulling it in both a posterior direction and a circumferential direction. Traction in a perpendicular direction pulls the retina toward the center of the vitreous cavity, narrowing the funnel of retinal detachment over the optic disk. In the napkin ring configuration, traction in a circumferential direction gathers the posterior retina together anterior to the optic disk. With irregular folds, traction is mainly perpendicular to the retinal surface, elevating the retina toward the center of the vitreous cavity. Irregular folds are present in the retina immediately behind the vitreous base, and the adjacent posterior hyaloid is contracted. The anterior retina within the vitreous base is stretched inward to form a fold in the coronal plane because circumferential contraction exerted along the concavity of the retina produces a secondary traction vector perpendicular to the retinal surface, toward the center of the vitreous cavity. The anterior retina is pulled in a perpendicular direction toward the center of the vitreous cavity. Radial folds are also formed as a result of contraction in a circumferential direction. The anterior retina is pulled forward as a result of contraction in an anteroposterior direction of the posterior hyaloid, the anterior hyaloid, and the vitreous base that remain after vitrectomy. Relief of retinal traction is most directly achieved by posterior vitrectomy and removal of preretinal and subretinal membranes. In most instances, scleral buckling is performed in conjunction with vitrectomy if there is no preexistent buckle. Relaxing retinotomies or retinectomies are considered if the above measures are insufficient to relieve traction, usually in cases with severe subretinal proliferation or vitreous base contraction. Contraction of the posterior hyaloid (located more posteriorly than usual in this case, as indicated by the line of pigment immediately behind its insertion inferiorly) creates a circumferential fold in the coronal plane.
Hen Bell (Henbane). Olmesartan.
- Spasms of the digestive tract, including the stomach and intestines.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Treating scar tissue, when the leaf oil is used on the skin.
- Dosing considerations for Henbane.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Henbane work?
- What is Henbane?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96126
The instrument rests on the lateral orbital rims and the observer stands a maximum distance from the mirrors arteria carotis communis order 20 mg olmesartan otc. The direction of globe displacement typically suggests one or several possible anatomical structures of origin. Since most orbital mass lesions occur in the superior orbit, the eye is often displaced downward. Lesions situated in the medial orbit, such as an ethmoid mucocele or subperiosteal abscess, will displace the globe laterally. There are very few anatomic structures in the inferior orbit that can be associated with a mass lesion so that upward displacement is relatively uncommon. Such lesions include metastatic tumors to the inferior rectus muscle, maxillary sinus tumors invading the orbit, or orbital floor hematomas associated with previously placed implants for blow out fracture repair. Along their course they are invested with a thin connective tissue sheath that is part of the vast orbital fascial connective tissue system. Mass lesions or inflammatory processes in the orbit that expand or restrict these fascial layers may exert traction on various ocular muscles resulting in motility disturbance and subjective diplopia. This can be manifest as a gross misalignment of the globes in primary gaze, or it may be appreciated only in extreme positions of gaze. Less commonly neuropathic ophthalmoplegia may result from malignant tumor infiltrating or compressing cranial nerves that supply the extraocular muscles, either in the orbital apex or in the cavernous sinus. Occasionally, diplopia may be the initial symptom of orbital disease before any other findings become obvious. Abaxial proptosis with the eye displaced downward and outward from an expanding subperiosteal hematoma along the superomedial orbital wall. When present it is often associated with compression of the optic nerve by intrinsic lesions such as meningiomas or optic nerve gliomas. In these cases visual loss is usually quite severe, associated with decreased color vision and an afferent papillary defect. Similarly, vision loss may be profound with small nonneural tumors located in the orbital apex, such as a hemangioma. Benign tumors in the mid-orbital muscle cone rarely cause visual problems unless they become very large. Even when very large, most slow-growing benign tumors such as cavernous hemangiomas and schwannomas do not cause significant pain, although the patient may complain of some pressure behind the eye. Pain is also a feature of some malignant tumors that show perineural spread, such as adenoid cystic carcinoma of the lacrimal gland. Inflammatory signs include erythema, edema, chemosis, dilated vessels, and tenderness. Most benign and malignant tumors, cysts, and structural vascular anomalies occur in only one orbit.
Specifications/Details
Campbell D arrhythmia practice tests olmesartan 20 mg purchase visa, Vela A: Modern goniosynechialysis for the treatment of synechial angle-closure glaucoma. Nonaka A, Kondo T, Kikuchi M, et al: Angle widening and alteration of ciliary process configuration after cataract surgery for primary angle closure. Hollows F, Graham P: Intraocular pressure, glaucoma, and glaucoma suspects in a defined population. Lowe R: Comparative incidence of angleclosure glaucoma among difference national groups in Victoria, Australia. Pollack I: Chronic angle closure glaucoma: diagnosis and treatment in patients with angles that appear open. Lamping Since the early 1900s, classification of the glaucomas has been based on anterior chamber depth and the status of the angle, as observed with a gonioscope. In 1938, Barkan observed that increased tension could result from permanent adhesions in the angle caused by contact between the peripheral iris and the trabecular meshwork; this observation marked a great step forward. In cases of primary wide-angle glaucoma in which the diagnosis could be established in one eye by the usual clinical methods, obstruction to flow was also present in the fellow eye, which to date had shown no clinical evidence of the disease. During a phase of elevated tension in narrow-angle glaucoma when the angle was closed, as observed gonioscopically, obstruction to outflow was proportionate to the height of the tension and to the degree of angle closure. Both Barkan and Chandler considered pupillary block to be the product of contact between the iris and the lens. Sugar7 stated that the posterior directed vector of force exerted by the iris sphincter was responsible. Mapstone8 provided rigorous mathematical analysis to explain the pupillary block mechanism. We are now fully aware that the primary angle-closure glaucomas develop in the presence of pupillary block, restricting the passage of aqueous humor from the posterior to the anterior chamber. This pressure differential balloons the peripheral iris forward into contact with the trabecular meshwork. Any of these changes in an eye with a narrow angle would lead to the diagnosis of primary angle closure. Chronic primary angle closure with pupillary block has also been referred to as creeping angle closure11 and shortening of the angle. Primary angle-closure glaucoma may occur when an increased obstruction to aqueous outflow, caused by a ballooning of the peripheral iris against the trabecular meshwork, results in permanent synechial closure. A reported 24 to 72% of patients will experience an elevated pressure in the postoperative period after an iridectomy for an acute angle-closure attack. Because this rise may not occur for months, the patient should be warned and followed regularly. Because repeated attacks of acute or subacute angle closure may permanently damage the trabecular meshwork, combined-mechanism glaucoma may also exist in the absence of visible peripheral anterior synechiae.
Syndromes
- Sudden and severe reactions, including those involving the eye, nose, throat, and lower respiratory tract
- Difficulty paying attention (attention deficit)
- Toe walking
- Are there tiny red or purple spots on the skin (petechiae)?
- Surgery is rarely done if the aneurysm is small.
- Use of a breathing tube for a long time
Hertel exophthalmometry measures the protrusion of the eyes as the distance from the lateral orbital rim to the anterior corneal surface blood pressure zona plus order olmesartan 10 mg otc. Some orbital inflammations may be bilateral either simultaneously or sequentially (Table 226. Distribution of common orbital mass lesions by the nature of onset from catastrophic to chronic. This can often provide useful information on the probable nature of the disease process. Chronic onset, over many months to years, is more likely associated with slow growing lesions such as neurogenic tumors, vascular tumors, and lymphoproliferative disorders. Dermoid cysts, for example, can be seen into middle age, but the vast majority present within the first decade of life. Other lesions such as lacrimal gland tumors, metastatic carcinomas, and cavernous hemangiomas more commonly present in adulthood. Orbital lymphoma is a disease seen almost exclusively in patients beyond the fourth to fifth decade. Orbital varix: (a) resting appearance showing a mild mass effect in the superomedial orbit, (b) with Valsalva the lesion expands from increased venous pressure. Pulsating proptosis may be seen with bony defects in the orbital roof in patients with orbital neurofibromatosis. Similarly, Valsalva associated with crying can cause enlargement of a mass with increased proptosis from a capillary hemangiomas in young children. Intermittent proptosis exacerbated with upper respiratory infections is characteristic of orbital lymphangiomas. Such studies may contribute to a specific diagnosis, and often provide guidance in planning the most appropriate medical therapy or surgical approach. The most common of these is eyelid retraction with a widening of the palpebral fissure. Contralateral eyelid ptosis from any one of numerous causes may make the involved eye look smaller due to a reduced palpebral fissure. This can be interpreted as an abnormal widening of the eyelids and therefore proptosis of the opposite eye. As the X-ray beams traverse tissue they are attenuated according to the density of the tissues through which they pass, and this attenuation is proportional to the relative density of the tissue with respect to the passage of X-rays. Less dense tissues, such as water, allow more X-rays to pass through producing a darker region on the final image.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: q._h.
Tags: purchase olmesartan 10 mg visa, 10 mg olmesartan with mastercard, purchase olmesartan 10 mg on-line, discount olmesartan 40 mg without a prescription
Customer Reviews
Muntasir, 47 years: The ends and posterior boundaries are irregular and sharply defined, whereas the anterior limits are less precise. Ammann F, Klein D, Franceschetti A: Genetic and epidemiological investigation of pigmentary degeneration of the retina and allied disorders in Switzerland. This silicone oil technique with its high reattachment rate may have entailed some compromise of the crystalline lens.
Vasco, 23 years: Also, timolol is available in a hemihydrate formulation, a formulation in gelforming solution that provides advantages for once-daily dosing, and a new timolol maleate solution formulated with potassium sorbate, allowing for enhanced bioavailability and once-daily dosing. It consists of collagen filaments intermixed with glycoproteins (laminin and fibronectin) and proteoglycans. Familial cases are rare, and there is no consistent association with any other ocular or systemic disorder.