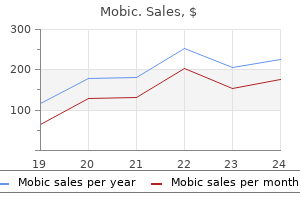
Only $0.23 per item
Mobic dosages: 15 mg, 7.5 mg
Mobic packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 240 pills
In stock: 838
9 of 10
Votes: 43 votes
Total customer reviews: 43
Description
Patients will present with arteriovenous nicking zostrix arthritis pain relief cream order mobic 15 mg visa, copper or silver wiring of the arteries, microaneurysms, hemorrhages, exudates, and cotton-wool spots. The patient was admitted to the hospital to treat malignant hypertension aggressively. Also note the blurred disk margin, the dllatlon and tortuoslty of the venules, and the cotton-wool spots. Thus, any patient presenting with these signs and symptoms should have their blood pressure taken immediately while still in the office. Treatment is focused on the controlled lowering and maintenance of blood pressure because patients are at higher risk of multiple vision-threatening conditions (eg, retinal vein occlusion, ischemic optic neuropathies, worsening diabetic retinopathy) and life-threatening conditions (eg. This is the location where the retinal nerve fiber layer exits the eye and becomes the myelinated optic nerve. Patients will present with a sudden change in vision, and examination will reveal dilation and tortuosity of the retinal veins, extensive retinal hemorrhages in a114 quadrants, disk edema, and/or macular edema. It is not uncommon for patients to present with temporary vision loss (typically <30 minutes) in 1 eye. Because the retina is a neurosensory organ, temporary loss of blood flow can cause loss of function, but as long as blood flow is restored in a reasonable time frame, vis. Although amaurosis fugax can be due to a variety of etiologies, the most common is embolic occlusion of the central retinal artery or 1 of its branches. Emboli are commonly from the carotid artery but may originate in the heart, heart valves, or aorta. The most common types of emboli are cholesterol (Hollenhorst) plaques, platelet fibrin, and calcium. Dilated examination should be focused on looldng for an embolus, typica11y at an arterial bifurcation point. If giant cell arteritis is suspected, sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein values should be determined. Otherwise, initial workup should include carotid Doppler and cardiac echocardiography to look for an embolic source. In these patients, the embolic event does not self-resolve or the occlusion maybe from another cause, such as thrombosis, giant cell arteritis, hypercoagulable states (eg. Vision loss is thought to become permanent after approximately 90 to 120 minutes of nonperfu. In addition to causing embolic events, severe carotid artery stenosis can also cause global hypoperfusion of the entire eye.
Myrtus communis (Myrtle). Mobic.
- Lung infections including bronchitis, whooping cough, and tuberculosis; bladder conditions; diarrhea; worms; and other conditions.
- How does Myrtle work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Myrtle.
- What is Myrtle?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96555
Although the pigment cell layer becomes firmly fixed to the choroid arthritis in feet uk 15 mg mobic buy mastercard, its attachment to the neural layer is not firm. The edema is viewed during ophthalmoscopy as swelling of the optic disc, a condition called papilledema. The central artery and vein of the retina cross the subarachnoid space and run within the distal part of the optic nerve. The pigment cell layer of the retina develops from the outer layer of the optic cup, and the neural layer develops from the inner layer of the cup. Forebrain Optic stalk Optic vesicle Lens placode Optic cup Ectoderm (A) Optic stalk Intraretinal space Invaginating lens vesicle Lumen of optic stalk (B) Outer layer of optic cup Ectoderm Presbyopia and Cataracts As people age, their lenses become harder and more flattened. These changes gradually reduce the focusing power of the lenses, a condition known as presbyopia (G. Some people also experience a loss of transparency (cloudiness) of the lens from areas of opaqueness (cataracts). Cataract extraction combined with an intra-ocular lens implant has become a common operation. Sclera Conjunctival sac Eyelid Anterior chamber Iridopupillary membrane Cornea Ectoderm Iris Glaucoma Outflow of aqueous humor through the scleral venous sinus into the blood circulation must occur at the same rate at which the aqueous is produced. This muscle is opposed most of the time by gravity and is the antagonist of the superior half of the orbicularis oculi, the sphincter of the palpebral fissure. The deep lamina of the distal (palpebral) part of the muscle includes smooth muscle fibers, the superior tarsal muscle, that produce additional widening of the palpebral fissure, especially during a sympathetic response. However, they seem to function continuously (in the absence of a sympathetic response per se) because an interruption of the sympathetic supply produces a constant ptosis-drooping of the upper eyelid. Absence of these movements resulting from nerve lesions contributes to double vision. Movements may occur around the three axes simultaneously, requiring three terms to describe the direction of movement from the primarily position. Rotation of the eyeball around the vertical axis moves the pupil medially (toward the midline, adduction) or laterally (away from the midline, abduction). Rotation around the transverse axis moves the pupil superiorly (elevation) or inferiorly (depression). Structures that enter the orbit through this canal and the adjacent part of the fissure lie initially within the cone of recti. Because they mainly run anteriorly to attach to the superior, inferior, medial, and lateral aspects of the eyeball anterior to its equator, the primary actions of the four recti in producing elevation, depression, adduction, and abduction are relatively intuitive.
Specifications/Details
It usually affects the dominant hand arthritis in my left knee cheap 15 mg mobic otc, but it can affect both hands, with severity being greater on the dominant side. Factors that promote the development of carpal tunnel syndrome include hormonal changes (menopause, pregnancy), weight gain, hypothyroidism, and diabetes mellitus. Patients commonly experience pain and paresthesia that do not always follow the distribution of the median nerve in the hand. The sensory symptoms are worse at night, and patients usually wake up from sleep and shake their hands trying to get some relief. On examination, there is usually decreased sensation in the palmer aspect of the lateral 3~ fingers. A positive Tinel sign refers to paresthesia in the radial portion of the palm and the radial fingers induced by a tap on the transverse carpal ligament. Paresthesia in the fingers can sometimes be induced by sustained passive hyperflexion of the wrist (Phalen sign). Treatment should start with splinting the wrist at a neutral position for few months. If there is no improvement, patients should be referred to a surgeon for either open or endoscopic carpal release surgery via transecting the flex. Alcoholism-Associated Neuropathy Alcoholism is most commonly associated with the development of a progressive painful axonal sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Thus, epidemiologic quantification of alcohol-associated neuropathy has been very challenging. Treatment of alcoholismassociated peripheral neuropathy requires abstinence and a well-balanced diet. Indeed, given that alcohol was shown to be a neurotoxin, it is important to counsel any patient with an established diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy, regardless of its etiology, on moderation of alcohol intake. Lead-Induced Neuropathy the incidence of lead toxicity with peripheral neuropathy has substantially been lowered with the declining human exposure to the known environmental major sources, such as leadbased paint and lead addition to gasoline. Lead neurotoxicity can present as a combination of motor-predominant peripheral neuropathy (as seen when the radial nerve is involved, leading to wrist and finger drop) and encephalopathy. There is often concomitant constipation secondary to autonomic nerve involvement Extraneural manifestations include microcytic hypochromic anemia and basophilic stippling of red blood cells. Measurement oflead level in a 24-hour urine collection Ulnar Mononeuropathy at the Elbow (Cubital Tunnel Syndrome) Ulnar nerve palsy is often traumatic in origin as the nerve is vulnerable to external compression at the level of medial epicondyle, the "funny bone. However, the sensory deficit is more often on the ulnar border of the hand rather than the forearm or arm. Conservative treatment with an elbow pad can be tried first, especially when sensory symptoms predominate. If there is no response, ulnar transposition surgery to transfer the nerve to the volar aspect of the elbow can be performed. Elbow extension is preserved as the branch that supplies the triceps comes out of the radial nerve proximal to the spiral groove. The sensory deficit is localized to the radial portion of the dorsum of the hand (anatomic snuffbox).
Syndromes
- pg/cell = picograms per cell
- For infections, you will need antibiotics from your doctor. Symptoms of a possible infection include burning or pain with urination, frequent urination, cloudy urine, and a sense of urgency (strong, sudden urge to urinate).
- Atrial fibrillation
- If you have diabetes, heart disease, or other medical problems, your surgeon will ask you to see your regular doctor.
- Do NOT make a person throw up unless told to do so by poison control or a health care professional.
- Severe change in acid level of blood (pH balance), which leads to damage in all of the body organs
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Pale skin
- Are stressed and exhausted
As the arteries begin to descend arthritis knee treatment naturally 15 mg mobic buy with visa, they travel deep to the middle of the clavicles and cross the superior surface of the 1st rib. The subclavian artery is divided into three parts by the anterior scalene muscle: (1) medial, (2) posterior, and (3) lateral. The artery then passes through the foramina of the transverse processes of vertebrae C1C6. This vertebral part of the vertebral artery may enter a foramen more superior than the C6 vertebra. The suboccipital part of the vertebral artery courses in a groove on the posterior arch of the atlas before it enters the cranial cavity through the foramen magnum, demarcating the beginning of the cranial part of the vertebral artery. The internal thoracic artery has no branches in the neck; its thoracic distribution is described in Chapter 1. The thyrocervical trunk arises from the anterosuperior aspect of the first part of the subclavian artery, near the medial border of the anterior scalene muscle. Arising from the cervicodorsal trunk are the dorsal scapular and superficial cervical arteries, sending branches to muscles in the lateral cervical region, the trapezius, and medial scapular muscles. The terminal branches of the thyrocervical trunk are the inferior thyroid artery, the primary visceral artery of the neck, and the ascending cervical artery, supplying lateral muscles of the upper neck. The costocervical trunk arises posteriorly from the second part of the subclavian artery (posterior to the anterior scalene muscle on the right side and usually just medial to this muscle on the left side). The dorsal scapular artery often arises from the cervicodorsal trunk, but it may be an independent branch of the second or third part of the subclavian artery. It runs deep to supply the levator scapulae and rhomboid muscles, supplying both and participating in the arterial anastomoses around the scapula (see Chapter 6). The sympathetic trunks receive no white rami communicantes (communicating branches) in the neck. The cervical portion of the trunks contains three cervical sympathetic ganglia: superior, middle, and inferior. These ganglia receive presynaptic fibers conveyed to the sympathetic trunk by the superior thoracic spinal nerves and their associated white rami communicantes, which then ascend through the sympathetic trunk to the ganglia. After synapsing with the postsynaptic neuron in the cervical sympathetic ganglia, postsynaptic neurons send fibers to the · Cervical spinal nerves via gray rami communicantes · Thoracic viscera via cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves · Head and viscera of the neck via cephalic arterial branches, which accompany arteries (especially the vertebral and internal and external carotid arteries) as the sympathetic periarterial plexuses the inferior cervical ganglion usually fuses with the first thoracic ganglion to form the cervicothoracic ganglion (stellate ganglion). Some postsynaptic fibers from the ganglion pass via gray rami communicantes to the anterior rami of the C7 and C8 spinal nerves. Other fibers pass to the heart via the inferior cervical cardiac nerve (a cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerve), which passes along the trachea to the deep cardiac plexus.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: p.o.
Tags: discount 7.5 mg mobic fast delivery, mobic 15 mg buy free shipping, 15 mg mobic purchase with visa, discount mobic 15 mg buy line
Customer Reviews
Curtis, 28 years: Underneath the cerebellar Purkinje neurons are a population of neurons called Lugaro cells.
Candela, 49 years: The process of rolling or turning an injured patient while maintaining spine precautions is often called "logrolling.
Kasim, 25 years: The ventricles originate as the inside or lumen ofthe neural tube during fetal development.
Felipe, 26 years: Behind the clavicle, each of 3 trunks bifurcate into anterior and posterior divisions.
Garik, 38 years: As such, the day-night cycle is a critical environmental factor shaping the evolution oflife on Earth.