Only $0.22 per item
Inderal dosages: 80 mg, 40 mg
Inderal packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 822
8 of 10
Votes: 311 votes
Total customer reviews: 311
Description
Preoperative planning and designing of a fluorocompatible endourology operating room blood pressure medication olmetec side effects inderal 40 mg order. Relationships between entrance skin dose, effective dose and dose area product for patients in diagnostic and interventional cardiac procedures. Committee to Assess Health Risks from Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation. During the past decade, as minimally invasive techniques have proliferated, reimbursements for hospital-based procedures have diminished, while reimbursements for office-based procedures have increased. Physicians in private practice have increasingly sought to perform procedures in the office. Urologists also found transurethral needle ablation using radiofrequency energy and interstitial laser coagulation could be performed with local anesthesia in the office [24]. Currently, urologists are performing and developing techniques for safe and comfortable laser ablation of the prostate in the office setting. Such a trend may change as reimbursement changes; nevertheless, an in-office procedure has a potential to be safer (in that only local anesthesia is used), more convenient and efficient for the patient. Such procedures are also less costly overall, saving on hospital/surgery center fees and professional anesthesia charges. Urologic outcomes should be similar to procedures performed in the hospital or surgery center with full anesthesia or intravenous sedation. True evidence-based conclusions comparing procedures performed with anesthesia and anesthetic monitoring to those performed under local anesthesia in the office do not exist. This chapter will discuss the common pharmacologic agents that can be used as local anesthetics, and the application and techniques used to deliver local anesthesia. It is hoped that the information presented will stimulate proper study for the development of improved local anesthetic protocols and techniques. Patient selection and preparation In order to enhance the likelihood of patient acceptance and comfort, preoperative counseling is paramount. Patient size, prostate size, and patient comfort level with the office physical examination and preoperative counseling need to be taken in to account. Patients should be counseled on the likelihood that they will not be fully anesthetized such that they will not be numb to all feeling. Some discomfort should be expected but this should be mild and generally well tolerated. Time should be spent explaining the delivery technique of the local anesthetic so that patients know what to expect.
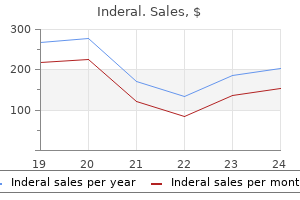
Althaea officinalis (Marshmallow). Inderal.
- Dosing considerations for Marshmallow.
- How does Marshmallow work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Sores, skin inflammation, burns, wounds, insect bites, chapped skin, diarrhea, constipation, stomach and intestinal ulcers, irritation of the mouth and throat, dry cough, and other conditions.
- What is Marshmallow?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96755
A 19-year-old man arrives by police drop-off with a gunshot wound to the right thigh xopenex arrhythmia generic inderal 80 mg line. He has a history of hypotension in the field, but on arrival at the trauma bay he is hemodynamically stable. His physical examination is notable for a single wound in proximity to the course of the superficial femoral artery and vein, which is not actively bleeding. Distal pulse evaluation reveals 2+ dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses bilaterally. Plain films reveal no fractures and a retained foreign body in the lateral aspect of the thigh. The patient can be safely discharged from the trauma bay without further diagnostic because the patient does not have any evidence of vascular "hard signs" B. Further diagnostic testing for vascular trauma is indicated, because the patient has a sensory defect suggestive of femoral nerve injury C. The patient can be safely admitted and observed because the patient has no hard signs and a normal peripheral pulse examination D. Further diagnostic testing for vascular trauma is indicated, because the patient has a history of hypotension in the field E. Further diagnostic testing for vascular trauma is indicated, because the trajectory of the projectile appears to be in proximity to the major vascular structures in the thigh the presence of a vascular "hard sign" (pulsatile bleeding, expanding hematoma, palpable thrill, audible bruit, loss of pulse) is specific for major vascular injury and mandates operative explo- ration, but absence of hard signs does not reliably exclude injury. Because of concern over limb-threatening consequences a result of missed injury, historically there has been a low threshold for operative exploration when the diagnosis of peripheral vascular injury was entertained. High rates of negative exploration lead to liberal use of angiography as an alternative, but this too was associated with a high rate of studies that demonstrated either no injury or injuries that did not require intervention. It is generally accepted that in the absence of hard signs a normal peripheral vascular examination does not require further investigation, even in the presence of vascular soft signs. When angiography is performed under these circumstances, roughly 10% of patients will be found to have an injury, but the natural history of the vast majority of these "minimal vascular injuries" is to resolve without intervention. Physical examination in conjunction with a 24-hour period of observation has been shown to have a false negative rate of less than 1% for major vascular injury, comparable to that of angiography. A 44-year-old man presents to the trauma bay with a crush injury to his left lower extremity after being run over by a tractor. On physical examination, there is a contaminated open wound on the left thigh associated with an obvious deformity. Regarding the management of this injury complex, which of the following is correct The addition of skeletal injury to arterial injury does not confer an increased risk of extremity amputation B. Limb salvage rates are equivalent whether revascularization or orthopedic stabilization is performed first C. When definitive vascular repair is performed prior to orthopedic stabilization, manipulation of the extremity leads to need to revise the vascular repair in the majority of cases D. In limbs at high risk for amputation, limb salvage and amputation are associated with similar functional outcomes at 2 years of revascularization need not be definitive. In the setting of hemodynamic instability, severely unstable or comminuted fractures, or gross contamination, intraluminal shunting should be considered as bridge to definitive vascular repair.

Specifications/Details
It is most commonly related to the calibration balloon being overinflated at the gastroesophageal junction B blood pressure medication depression trusted 40 mg inderal. Intraoperative endoscopy is not useful in detecting a posterior perforation after the band is placed. Once the perforation is repaired, band placement should proceed as planned to cover the repaired defect D. If not recognized intraoperatively, it presents as abdominal pain, fever, or sepsis one or two days after band placement. If not recognized intraoperatively, it presents as gastric outlet obstruction several months after band placement. Most intraoperative gastric perforations during band placement occur during the creation of the retrogastric tunnel. The blunt instrument used to create the tunnel should pass without resistance from the base of the right crus to the angle of His after the appropriate peritoneal surfaces have been dissected. Intraoperative findings that should alert the surgeon to a posterior perforation include unexplained bleeding from the tunnel or bile staining, especially if there have been repeated attempts to pass the instrument through the retrogastric tunnel. When a perforation occurs it should be identified intraoperatively and repaired primarily. Intraoperative endoscopy is a valuable tool to aid in the detection and location of a perforation. In this situation, band placement should be abandoned and not re-attempted for several months. Most patients are discharged within 24 hours of band placement, so a missed perforation will result in abdominal sepsis when the patient returns to the emergency department 24 to 48 hours after discharge. These patients will require aggressive fluid resuscitation, antibiotics, laparoscopic or open removal of the band, primary repair of the perforation if possible, and wide local drainage. Which of the following is/are true regarding gastric perforation during laparoscopic adjustable band placement Schirmer B, Erenoglu C, Miller A (2002) Flexible endoscopy in the management of patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. A 50-year-old woman underwent a laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass one year ago and now presents with severe epigastric pain and blood in her stool. Gastroscopy shows a very small proximal gastric pouch (<15 ml) and a gastrojejunal stomal ulcer. Possible contributing factors to marginal ulcer formation include all of the following except: A. Gastro-gastric fistula Gastrojejunal ulceration after gastric bypass has been associated with a foreign-body reaction at the anastomosis, particularly when nonabsorbable suture erodes in to the lumen. Ulcers at the site of the gastrojejunal anastomosis complicate between 1% to 16% of gastric bypasses with the highest risk in the first three months after surgery. The etiology is often multifactorial and this complication has been associated with use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, nonabsorbable suture material, a gastric pouch size larger than 50 ml, Helicobacter pylori, and excessive acid exposure in the gastric pouch from a gastro-gastric fistula. Alcohol and smoking have also been causally implicated in patients with marginal ulcers.
Syndromes
- Sexual activity during adolescence
- Repeats words or memorized passages, such as commercials
- Antibiotics to treat any infection
- How to recognize when a chronic medical problem is getting worse
- Allergies
- For girls, place the bag over the labia.
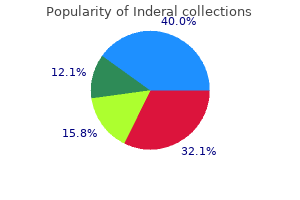
A large multicenter prospective observational trial identified severe fecal contamination blood pressure and anxiety inderal 80 mg purchase on-line, transfusion of 4 units of blood or greater, and inappropriate antibiotic prophylaxis as independent predictors of postoperative complications. It also found that the method of repair had no effect on the rate of complications. Several other studies have supported these findings, and additionally identified blood loss greater than 1 L, and hypotension as being risk factors for infectious complications. Lastly, several studies have found no additional benefit to continuing antibiotic coverage beyond 24 hours postoperatively regardless of the extent of contamination. Injuries due to blunt trauma in this area are unlikely to require surgical repair and hematomas should be left intact. Following penetrating trauma, major vascular or hollow viscous injuries are common and all hematomas should be explored. However this is less likely following blunt trauma and the risk of releasing venous hemorrhage is high. Most bleeding associated with pelvic fracture following blunt trauma is not amenable to surgical correction and is more likely to respond to interventional techniques or pelvic stabilization. Tamponade is possible even with major vascular injury in this area, and release of tamponade can result in exsanguinating hemorrhage. Stable hematomas resulting from both penetrating and blunt trauma in this area should not be explored. Retrohepatic trauma hematoma following penetrating Zone I hematomas are centrally located and contain the major abdominal vessels, because of this vascular injury is highly suspected and Zone I hematomas due to both blunt and penetrating trauma should be explored. Of the following, which is/are taken in to account when considering damage-control laparotomy and temporary abdominal closure It has since been applied to many surgical conditions including nontraumatic abdominal surgery, vascular surgery and orthopedic surgery. First, control of acute hemorrhage and contamination, second resuscitation, and third planned re-exploration for definitive treatment of surgical pathology. Which of the following methods is an option for temporary abdominal closure in primary damage-control surgery Additionally as there may be significant drainage from the abdominal cavity the closure method must have a means of collecting, removing and quantifying this drainage. Methods that reapproximate fascia or skin may create abdominal compartment syndrome and should be taken in to account. There are some surgeons that prefer to approximate the skin over a suction system as it avoids the loss of domain. The two most popular techniques are vacuum-assisted abdominal dressings and the Bogota bag. Vacuum-assisted closure can be performed with commercially available materials, or following the Barker method. The Bogota bag uses sterile plastic sutured to the skin to create an abdominal silo. There is also the option of skin closure, or placement of absorbable mesh with planned ventral hernia. Many physicians also combine methods using a combination of dynamic retention sutures with Barker or other type of vacuum closure system in order to decrease the loss of abdominal domain. The second stage of damage-control surgery is aimed at correcting which of the following values Following splenectomy for trauma, vaccinations should be sure to include which of the following organisms Pseudomonas aeruginosa the spleen produces tuftsin and properdin, postsplenectomy patients have diminished immunity and are most at risk for infection from encapsulated organisms.
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: ut dict.

Tags: 40 mg inderal order free shipping, 80 mg inderal order otc, safe 80 mg inderal, discount inderal 80 mg otc
Customer Reviews
Grok, 48 years: Although relatively uncommon, occurring after 115% of Roux-en-Y gastric bypasses, marginal ulceration can be a challenge to diagnose and treat. Although this equation may not accurately describe the flow state in our circulatory system, it has useful applications in describing flow through catheters, flow characteristics of different resuscitative fluids and the hemodynamic effects of anemia and blood transfusions on flow. Which of the following is not an advantage of continuous renal replacement therapy over intermittent dialysis Better removal of proinflammatory mediators Although the type of renal placement therapy, as well as the dosing of the dialysis remains controversial, there are some circumstances in which continuous renal replacement therapy such as continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration offers advantages over intermittent hemodialysis. Under the influence of testosterone from the leydig cells of testes, the Wolffian ducts form the epididymis, vas deferens and seminal vesicles (male internal genitalia).
Steve, 39 years: At a bladder volume of approximately 400 mL, the patient had a voluntary detrusor contraction. Many filters exist and there seems to be a trend toward placement of retrievable filters despite poor retrieval rates. When utilizing injection anesthetic, it is important to be aware of the maximum dosage as overdosing may result in significant adverse events. A Glasgow Coma Scale Score of 7 (intubated) with a measured intracranial pressure of 8 mm Hg, a midline shift of 2 mm, and a mass lesion measuring 8 cm3 D.
Yugul, 50 years: Despite having an osmolality of 200 mOsm/kg, it has played a role in reducing the risk of hemolysis and death by more than 50% from the days when distilled water was used for irrigation [9]. Lowering the sympathetic drive with increased sedation will lead to severe hypotension and worsening shock. Any enlargement of the ovary should be considered as malignancy until proven otherwise. Finally, the patient should be informed that remaining tissue can grow back, causing recurrent voiding symptoms, and that additional prostate surgery may be required.